Motor points of muscles for electrical stimulation. Electrical stimulation: indications, contraindications, methods, side effects. Devices for electromyostimulation
The human body is capable of self-healing, but sometimes (after injuries, surgeries) this can take quite a long time. For successful and faster recovery in medicine, various are used. Therefore, we will further analyze what electrical stimulation of the back muscles is, how it is useful and how it is carried out.
The technique is widely used for the rehabilitation of patients after various types of illness, with disorders of the functioning of the nervous system, and with muscle hypertonicity.
Why is the procedure useful?
The benefits of current stimulation sessions are obvious. So, Using this technology allows you to achieve the following results:

The procedure shows high results in therapy
- Prevention of muscle tissue atrophy.
- Restoration of nutrition processes and elimination of metabolic products.
- Reducing pain of any localization.
- Increased adaptation and muscle fatigue limit.
- Promoting the process of tissue regeneration.
Regular stimulation also ensures recovery " feedback"with the cerebral cortex.
Thanks to this, the nervous regulation of muscle tissue contractions is gradually restored. This is a great achievement in the treatment of severe pathologies (paralysis, paresis).
Devices for the procedure
All devices for electrical muscle stimulation have a main unit in which a current of the required frequency and strength is generated, as well as electrodes attached to the body.
Reference. Each device has different operating modes necessary for a specific muscle group.
Devices are divided into several types according to their purpose:
- professional- used in medicine and cosmetology;
- low-power- intended for use at home.
Devices are also distinguished based on the nature of the outgoing currents:
- "Amplipulse-4.5", "Stimul-1"- for recovery and stimulation of muscles using sinusoidal currents of high frequencies, modulated by low frequencies.
- "Neuropulse", "UEI-1"- used for reduced electrical excitability of muscles. Currents flow in rectified mode.

Various devices have been developed for stimulating muscles with current.
There are many other devices in medicine, each of which has its own application features: “NET”, “Tonus-1”, “Myovolna”, etc.
Electrical stimulation at home
The technique is quite simple to perform, so you can perform electrical muscle stimulation at home.
The session flow includes several stages and looks like this:

Can be used at home
- the electrodes are moistened with water and placed on the affected muscle tissue and secured with bandages;
- wires are connected;
- a suitable program is launched on the device;
- the current strength increases in stages, 3-4 minutes after the start of the electric shock, until muscle contractions are felt;
- after the end of the session, the device is turned off and the electrodes are removed;
- The skin in the area where the electrodes are applied is treated with a tonic to moisturize.
It is imperative to study the instructions for the electrical muscle stimulator, which will ensure the correctness of the procedure and the effectiveness of the treatment.
If the technique of performing sessions is not followed, side effects may develop.
How often can the procedures be done? How often can you do electrical muscle stimulation? ? Treatment with a similar physiotherapeutic method is carried out 2-3 times a week
Reference., however, it is possible to conduct a session every other day (depending on the indications).
The therapeutic course includes 10-20 sessions. The duration of the procedure should be approximately 20-40 minutes. A repeat course can be taken no earlier than 1 month
after the previous one.

Side effects
There are practically no side effects
There are practically no side effects of electrical muscle stimulation. The only thing that can be noted is
a feeling of muscle discomfort during the session and after it.
Also, an inflammatory reaction may occur at the points of contact between the skin and the electrodes.
In order to avoid such undesirable reactions from the body, the patient must monitor his well-being during sessions. If discomfort occurs, even minor, the patient should inform the doctor.
The list of contraindications to electrical muscle stimulators is extensive. When prescribing therapy, it must be taken into account by the doctor. Important!
The procedure may accelerate the progression of some diseases, leading to undesirable consequences.

It is prohibited to carry out the procedure in the presence of the following circumstances and diseases:
- Has a large list of contraindications
- oncology;
- infectious diseases;
- epilepsy;
- hyperthyroidism;
- blood pathologies;
- heart failure above degree 2;
- active form of rheumatism
- presence of pacemakers;
- formations of a benign nature;
- atrial fibrillation;
- phlebitis, thrombophlebitis;
- violations of the integrity of the skin (abrasions, wounds, cuts);
- condition after suturing muscles, tendons, nerves (for 1 month).
This method of treatment should not be used in pregnant women., since the procedures can cause an increase in uterine tone, which can result in miscarriage or premature birth (depending on the stage of pregnancy).
Conclusion
Therapy for pathologies of the nervous and muscular system is impossible without physiotherapeutic techniques. Among the variety of procedures, electrical stimulation is the most active and shows high results in treatment.
Electrical muscle stimulation is a procedure that uses pulsed current to restore the functioning of tissues, organs and systems, including the nervous part of muscles, that have lost their natural functioning after illness and injury. Electrical stimulation devices are considered particularly important and significant in treatment for restoring the functioning of the nervous system to an optimal state, as well as if there are diseases that can lead to limited movement, decreased strength and muscle wasting. Stimulation of muscle tissue is carried out using targeted excitation and contraction of a certain group of muscles, and this is carried out simultaneously in order to enhance metabolic and trophic processes that are aimed at providing the muscles with an energy reserve. This treatment also involves increasing the activity of each of the regulatory systems, each point on the cerebral cortex.
At the moment when an electric current of a stimulating direction passes through the nerve trunks, the conductivity of nerve excitations increases, and the recovery of each damaged nerve can also noticeably accelerate.
With normal or artificial muscle contraction, muscle atrophy is inhibited, even if a diagnosis of complete disruption of nerve conduction is made. Muscle atrophy should be prevented as early as possible, or you will inevitably have to deal with the degeneration of muscle fibers into connective ones - those that are not able to contract on their own. An electrical stimulation device can improve the blood circulation process by dilating the blood vessel and increasing the speed of blood flow. For example, you can visually track such actions in the form of redness (hyperemia) or an increase in the temperature level on the skin under the electrode. Activation of lymph and blood circulation is carried out in the deep tissue of the interelectrode spaces; therefore, the permeability of the vascular tissue may be too high, which leads to the opening of reserve capillaries.

The occurrence of hyperemia occurs during electrical stimulation and if a direct effect is carried out on the walls of blood vessels through a biologically active substance formed in the stimulated tissue. Regardless of what needs to be treated - the muscles of the back, thighs or any other part of the body - you need to keep in mind that the activation of blood circulation during electrical stimulation can be the factor that provides many therapeutic effects. Namely, tissue nutrition will improve, products of impaired metabolism will be removed, including the resorption of edema, softening of the scar, if present, regeneration of damaged areas and improvement of blood circulation. Electrical stimulation is considered an excellent way to improve blood circulation and enhance the synthesis of nucleic acids in the body, which is especially important for the normal functioning of the body.
Indications for electromyostimulation
The muscles of the back, thighs and other parts of the body often need electrical stimulation and regulation of the central nervous system, and more precisely, the head and back. Electrical muscle stimulation helps restore the functioning of the neuromuscular apparatus, the tone of any muscle groups, and the overall muscle mass. This procedure also helps to increase the blood flow in arteries and veins. This process is also considered important for the analgesic effect.
There are many diseases that require electrical stimulation, and in some cases additional stimulation of the body at home may be required. Diseases can be very different, for example:
- peripheral paresis;
- paralysis;
- nerve plexus;
- nerve root.
In case of peripheral paresis and paralysis, flabbiness of the affected muscle area is monitored. There is another group of diseases, such as central paresis and paralysis after injury to the brain and spinal cord. The latter types of disease mainly manifest themselves in the form of thickening of muscle tissue.
A similar method of treatment is prescribed to people of different ages and even children with disorders in the central nervous system, after particularly severe trauma and with cerebral palsy.
Contraindications to the appointment of procedures
Each treatment method has its own advantages and contraindications, which you should pay attention to when visiting a doctor, since you can not only improve the condition, but also worsen it to unimaginable stages.
For example, if the body monitors the presence of chronic diseases of the heart, blood vessels, significant fractures, or the period after myocardial infarction. It is strictly contraindicated to use this method of restoring the body’s functioning if a pacemaker is installed, since the condition can worsen to a radically critical state. If there are specific contraindications, then they should not be neglected, since in such treatment you should listen only to doctors and their opinion. A competent approach to treatment will allow you to get a positive result. You need to take care of your health as best and carefully as possible, especially when it comes to the spinal cord and brain. Only in this case is it possible to avoid complete paralysis of the body and, accordingly, a quick death. It is impossible to recover from a certain disease using electrical stimulation, since a whole range of measures will be required to completely restore the body.
In this article we will tell you everything about an electrical stimulator for building muscle mass, an electric massager and electrophoresis in one device.
In 1990-1995, a big wave of bodybuilding swept through our country. Rocking chairs, which were usually located in the basements of houses, became widespread. Those who wanted to increase their muscle mass first rewrote and redrew, and then, with the spread of “bourgeois” copying technology, they photocopied notes and drawings describing the methods of building muscle mass by the then famous teacher of bodybuilders - Joe Weider. This wave did not pass me by either. In one of the cooperatives in Kyiv, I wrote out by cash on delivery the diagram and description of the “Electric stimulator for muscle building". I assembled this device and used it for some time instead of heavy sports equipment.
The remarkable property of this device is that with its help you can not only “pump up” muscles, but also do electromassage. This is achieved by setting the operating mode to short pulses. A person relaxes his body, while enjoying it - the muscles “themselves” twitch involuntarily. Bruises, sprains and dislocations when using an electrical stimulator heal faster due to the acceleration of metabolic processes in skin cells and muscle tissue.
The electrical stimulator allows burn subcutaneous fat.
Another property of the electrical stimulator is that it can be used in a physiotherapy room - work in a mode that allows you to perform a medical procedure - electrophoresis.
In sports practice, the use of electrical stimulation is recommended for:
- increased muscle strength (40-50%);
- increasing muscle volume (5-10%);
- improvement of speed qualities /up to 29%);
- reduction of the subcutaneous fat layer (10-15%);
- increasing muscle performance;
- increasing the elasticity of muscles and ligaments.
Digital data are given for a three-week course of electrical stimulation. It is advisable to use electrical stimulation to improve the above qualities, both for beginners and experienced athletes. The most pronounced positive effect of electrical stimulation is in bodybuilding, weightlifting, gymnastics, various types of martial arts, etc.
Main purpose of the device
A single-channel stimulator of the human neuromuscular system is intended for physiotherapeutic effects with pulse-modulated currents in health and sports practice, as a means of increasing functional physical sports performance, and for the purpose of preventing and relieving pain syndromes.
The output stimulating pulses (SI) of the device are rectangular current oscillations of adjustable frequency (1-10 kHz) modulated by an exponential envelope. Envelope repetition frequency 7-300 Hz. The indicated SIs are formed into bursts of pulses, adjustable in duration: 0.5-10 sec or 0.05-1 Hz.
Specifications
- In the continuous generation mode (toggle switches “AM”, “FM” - position “0”) a continuous series of SIs is formed, the amplitude of which is regulated by resistor R2 “Output Level”, and the repetition rate by resistor R1 “Pulse Frequency”.
- In amplitude modulation mode (the “AM” toggle switch is on), automatic alternation of SI series and pauses. The duration of the series is regulated by R3 “Modulation frequency”.
- In the frequency modulation mode (“FM” is on), a continuous series of SIs is generated, automatically varying in frequency from the value set by the regulator“Pulse frequency” to the minimum SI repetition rate.
- The SI amplitude regulation is smooth, from (0-3) V to (33- +3) V (at a power source voltage of (9- + 0.25 V).
- The SI repetition frequency is smoothly adjusted from (5.8) Hz to (355-+89) Hz.
- Regulation of the frequency of the modulating signal in the range from (0.05-+0.01) Hz to (0.9-+0.22) Hz (or, respectively, from 3 to 120 modulations / min).
- The ratio of the duration of the modulation pulse to the pause is no more than 1.5:1.
- The pulse duration (ti) is (0.5-+0.08) ms.
- Average power consumption (at power supply voltage (9-+0.25) V, SI amplitude (33-+3) V and connected load equivalent (1-+0.1) kOhm) does not exceed (1.2-+0 ,12)W
The schematic diagram of the electrical stimulator is shown in the figure below.
The stimulator consists of:
Generator of stimulating pulses on elements DD1.1, DD1.2, VD1, VD2, VT3, C1, R1...R7 and resistor R1 “Pulse frequency”;
Modulation generator using elements DD1.3, DD1.4, VT12, SZ, C4, R14…R16, R18…R21, R24 and resistor R3 “Modulation frequency”;
Filling frequency generator on elements DD2.1, DD2.2, VD13, VD14, VT15...VT17, C5, R22, R23, R25...R30, VT19, VT20 and resistor R4 “Filling frequency”;
Power amplifier based on elements VT18, VT21, VT22, R31...R35, C6, C7, transformer TV1, VD23;
Stabilizer on elements VT24, VT25, R36...R38 and LED H3;
Attenuator and pulse shaper on elements VT5, VT6, VD7...VD11, R10...R13, C2, R39 and resistor R2 “Output level”;
Display units on elements DD2.3, R8 and LED H1; VT4, R9 and pointer device PA1 (output signal setting level);
DD2.4, R17 and LED H2 (modulation frequency), LED NC (power supply voltage control).
The signal generators are assembled according to traditional circuits and do not require a separate description.
Electrical stimulator parts list
DD1, DD2 - K561LA7
VT3, VT4, VT17, VT18, VT24, VT25 - KT315G
VT5, VT21 - KT361G
VT19, VT20 - KT972A
VT22 – KT827A VD1, VD2, VD7, VD8…VD14, VD23 – D223B
N1, N2, N3 - AL307BM Device RA1 - M4248 - 100 µA
C1 - 0.068 µF
C2 - 4.7 nF
SZ - 50.0 µF x 10 V
C4 - 10.0 x 10 V
C5 - 6.8 nF
C6 - 30 pF
C7 - 200.0 µF
Transformer: Armor core diameter - 28 mm (external), 12 mm (internal), height - 24 mm. Windings I, II - 27 turns PEL-0.3, III - 447 turns PEL-0.2 The beginning and end of the windings are shown in the diagram.
Resistors:
R1, R33 - 1 kOhm
R2, R9, R14, R22, R23, R24 - 24 kOhm
R3 - 5.6 kOhm
R4 - 56 kOhm
R5, R10 - 100 kOhm
R6 - 68 kOhm
R11, R16, R18, R34 - 10 kOhm
R13 - 75 kOhm
R15 - 4.3 kOhm
R20 - 6.8 kOhm
R19 - 51 kOhm
R21 - 20 kOhm
R25, R26, R28, R35 - 3.3 kOhm
R27, R30 - 6.2 kOhm
R29 - 1.8 kOhm
R31, R37 - 4.7 kOhm
R32 - 100 0m
R36 - 910 Ohm
R38 - 510 Ohm
R39 - 1 kOhm
Variable resistors:
R1 SPZ-4A - 10 kOhm
R2 SPZ-4A - 4.7 kOhm
R3, R4 SPZ-4A - 100 kOhm.
The stimulator is assembled in a case the size of a regular school notebook and approximately 5 centimeters in height. The body was soldered from foil PCB and painted with quick-drying enamel. For better adhesion of the enamel to copper foil, the body was prepared before painting: lightly treated with coarse sandpaper, then placed in a ferric chloride solution for 1 minute, then washed and dried. To reduce the size, I used a recording indicator from a cassette recorder as a PA1 device. Battery power makes the device safe from electric shock (in an unexpected situation during procedures, a person will not be able to tear off the electrodes attached to the body). A compartment was made for two square 4.5 volt batteries, but I did not put batteries in it (you can’t get enough of them), but a 9 volt step-down transformer with a diode bridge and a 470 uF capacitor. This does not meet safety requirements, but by fulfilling certain requirements you can protect yourself by other measures - be “isolated” from heating systems, grounding, large metal objects in room.
Printed circuit board
- deltoid muscles 1;
- biceps 2;
- triceps 15;
- brachioradialis muscle 3;
- extensor radialis 14;
- trapezius muscle of the back 8;
- subscapularis and latissimus dorsi 9;
- teres major muscle 10;
- external oblique abdominal muscle 6;
- serratus anterior and rectus abdominis 5;
- gluteus medius, tensor fasciae lata, gluteus maximus 11;
- sartorius and rectus femoris 7;
- biceps femoris 13;
- semitendinosus muscle;
- semimembranosus muscle;
- calf muscle 12.
ATTENTION! It is not recommended to subject the pectoral muscles to electrical stimulation. To prevent current flow through the heart area, electrodes should always be placed only on the left or right, upper or lower parts of the body, but never on both sides.
To avoid unpleasant sensations during electrical stimulation, it is necessary to ensure reliable contact between the electrode area and the skin. To do this, place 6-8-layer gauze pads soaked in a 5-10% solution of table salt under the electrodes. The best results are obtained by powdered graphite with spindle oil (the consistency of sour cream).
1. Increased muscle strength and muscle size
To develop strength qualities, electrical stimulation of the muscle is carried out with the highest possible current (voltage), the value of which is individual and determined by personal sensations. There should be a feeling that the muscle is being torn. This effect is achieved in addition to increasing the amplitude of the signal, also by the duration of the effect. The muscle is brought to a state of complete fatigue by a series of messages: stimulation-relaxation. The duration of stimulation and relaxation is selected individually, observing the main criterion - rapid achievement of fatigue. Before starting the session, you should warm up all muscle groups. It is recommended to carry out training 1-2 times a day; with limited time, stimulation of the most important muscle groups is carried out. Electrical stimulation time for one muscle is up to 5 minutes.
ATTENTION: In the first days of classes, do not allow yourself to become overtired. The achieved results last for 3-4 months without continuing training.
2. Reduction of subcutaneous fat layer
Electrical stimulation allows you to reduce the thickness of the fat layer, activating metabolic processes throughout the body. For this purpose, stimulation is performed large groups muscles (gluteal, abdominal, etc.). The amplitude of the output signal is set to a painless and maximum tolerated muscle contraction. Course - 20 daily sessions, following a fasting diet. Session up to 10 minutes for each muscle group. Electrical stimulation is also effective for emphasizing muscle relief.
3. Flexibility training
The use of electrical stimulation allows for effective stretching of muscles and ligaments, which significantly reduces the time for mastering exercises that require flexibility (for example, “splits”). This area of application of ES can be recommended for representatives of various types of martial arts. To increase flexibility, electrodes are applied to those muscles whose “tension” does not allow performing a particular exercise (for example, the muscles of the back and front of the thigh when doing the splits). The signal amplitude is gradually increased from zero, the relaxation time should be equal to the stimulation time. You need to perform exercises that “stretch” the muscles and ligaments, the stretching of which determines the successful implementation, for example, of the same twine. The combination of exercise and electrical stimulation is very effective in developing flexibility. Work on each muscle for up to 5-10 minutes.
Rules for turning on and controlling the electrical stimulator
The “Output Level” knob should be moved to the far left position. Then, without connecting the electrodes, set the “Output Level” to maximum, switches AM to “1”, FM to “0”. In this case, the battery voltage indicator HL3 should light up; the HL2 modulation indicator lights up rhythmically; synchronously with it - the dial indicator deviates to the right. The HL1 pulse presence indicator should glow from low to moderate level (depending on the “Pulse frequency” knob).
Before starting the session, moisten the electrodes in a saline solution, securely attach the electrodes to the stimulated muscle, connect the wires coming from the electrodes to connectors X1 and X2 of the electrical stimulator. Turn on the electrical stimulator, use the amplitude regulator to gradually set the desired SI amplitude from zero, based on the training methodology and personal feelings. If tingling or burning occurs, press the electrodes harder against the muscles.
When performing electrical stimulation according to point 1, AM, FM is turned on, pulse repetition rate is 30-100 Hz, modulation frequency is 0.2-0.25 Hz (12-15 bursts per minute), filling frequency is 2-8 kHz. The optimal position of the adjustments is determined according to personal feelings, achieving the least discomfort. The rest is according to No. 1 of the Methodology.
For electrical stimulation according to point 2 of the Method: AM on, FM off, repetition rate 100-200 Hz, filling frequency 4-8 kHz, modulation frequency 0.5 Hz (30 bursts per minute).
When performing electrical stimulation according to clause 3, set the parameters according to clause 1 of the Methodology.
Nutrition
Electrical stimulation for the purpose of increasing muscle volume does not remove the athlete’s usual nutritional requirements for bodybuilding. Proper and balanced nutrition combined with electrical stimulation is the key to rapid muscle growth. The use of electrical stimulation to reduce the fat layer requires some dietary restrictions. Nutritional recommendations are not the scope of this manual; this issue is fairly well covered in sports and popular science literature.
Security measures
PROHIBITED:
— moving the electrodes during electrical stimulation without turning off the power of the device;
— break the electrical stimulator-electrode circuit during the session;
— start an electrical stimulation session without reducing the signal amplitude to zero;
- exercise in a state of extreme fatigue.
In terms of the method of protecting the patient from electrical voltage, the stimulator corresponds to class III and type BF according to GOST 12.2.025 - 76g.
There are no absolute contraindications to the use of electrical stimulation.
Electrical stimulation is relatively contraindicated in the following diseases: hemophilia, hereditary-familial diseases of the nervous system (progressive muscular dystrophy, myotonia, myasthenia, amytrophic lateral sclerosis, epilepsy, syrigomyelia, multiple sclerosis (in the acute phase), syphilitic tabes, infectious chorea, all infectious and non-communicable diseases in the acute stage, fever, disorders cerebral circulation, severe forms of hypertension, skin diseases, rupture of muscles and ligaments, bone fractures. Do not apply pressure to the vocal cords as airway closure may occur. Do not perform electrical stimulation of the abdominal and lumbar areas in pregnant women.
It should be borne in mind that electrical stimulation can suppress chronic pain, which is a symptom of a pathological process of unknown causes.
In all cases, the question of the advisability of electrical stimulation should be discussed with a medical specialist.
Electrical muscle stimulation is often used in physiotherapy and rehabilitation. The procedure has two purposes. First of all, the effect is aimed at eliminating pain. At the same time, muscle activity is restored. Next, we will consider this procedure in more detail. The article will also describe some devices for electrical muscle stimulation.
General information
Electrical muscle stimulation is performed using special equipment. It is equipped with electrodes that are connected using wires. A device for electrical muscle stimulation sends current to the elements. Through electrodes, impulses are distributed into muscle tissue. As a result, a motor or sensory reaction appears.
Electrode placement methods
They are placed on the surface of the skin, over specific muscles. There are two options for placing elements. The first is to place one electrode on a healthy area, and the second on the affected one. In the second case, the elements are placed on both sides of the problem area. The negative polarity that surrounds the damaged area promotes healing. It stimulates tissue formation, thus accelerating recovery processes.
Indications and contraindications
Electrical stimulation is recommended for the prevention of muscle atrophy, stimulation of the muscles of the thighs, large fibers of the anterior wall of the peritoneum with cellulite. The procedures are used to reduce excess weight and correct the figure. Electrical stimulation is recommended for deterioration of blood circulation (peripheral venous and arterial), decreased tone, and lymphatic drainage. The procedure is not prescribed if you are pregnant or have an intrauterine pacemaker. Electrical stimulation is contraindicated in cases of nervousness or after operations.

Relieving pain
There are two opinions about how electrical muscle stimulation relieves pain. According to the gate theory, the first hypothesis, signals from the affected area are sent to the brain through nerves. However, most of the impulses go through the "gate". Signals during electrical stimulation also pass through them. As a result, the nerves transmitting the pain impulse are blocked. According to another theory, electrical stimulation of muscles causes the brain to produce natural painkillers - enkephalins and endorphins. It has been established that after low-frequency exposure the content of these compounds increases.
Impact on atrophy
The decrease can accompany a variety of pathologies. Electrical muscle stimulation is often used to slow or prevent this process. The impulses sent by the device for electrical muscle stimulation help maintain the activity of weakened muscles.

Therapy for osteoarthritis
This pathology is caused by the degradation of articular tissues. Studies have found that electrical stimulation is very effective technique in the treatment of patients suffering from osteoarthritis in this area of the lower limb, as well as after surgery and joint replacement. Pulsing can help strengthen the knee extensors, which provides better mobility of the segment.
Prevention of bedsores
This problem is considered quite common for bedridden patients. Staying in this position for a long time puts strong and constant pressure on certain areas of the body. Electrical stimulation of the buttocks helps prevent deformities and bedsores.

Tissue repair
Electrical muscle stimulation is actively used on fibers that do not contract sufficiently. This type of effect is indicated for various conditions, but most often it is prescribed to patients who have suffered a stroke or orthopedic surgery. Often such patients experience serious difficulties when trying to make movements. When the electrodes are placed correctly, the electrical signal from the device is sent to the muscles and the fibers can begin to contract without the patient's intervention. During this artificially induced reaction, the patient also tries to contract the muscles. As a result, the procedures help the brain again “learn” to coordinate muscle activity on its own.
Electrical muscle stimulation: expert reviews
Despite the fact that various activities are periodically carried out to study the effects of electric shock, its effectiveness remains in question. In some studies, the procedure produces almost no results at all. Electrical muscle stimulation is often used as an alternative method due to insufficient evidence of its benefits. However, there are experts who indicate the effectiveness of the procedures. Thus, in one study conducted in 2014, which involved patients with severe and moderate muscle pain, it was found that exposure to electricity contributed to a significant reduction in the intensity of sensations. It should be noted that research into the effectiveness of the procedures is still ongoing.

Electrical muscle stimulation for children
In pediatrics, electric shock is often used. A procedure such as electrical muscle stimulation is not contraindicated for children, but has its own characteristics. First of all, you should be careful not to exceed the duration of exposure. Electrical stimulation of the lower leg muscles is prescribed for children with reduced tone. Due to the pulse effect, blood circulation is stimulated and muscle activity is restored. Electrical stimulation of the lower leg muscles is recommended for children with flat feet.
Benefits of exposure
Electrical muscle stimulation, reviews from many patients confirm this, is very effective in many cases. The undoubted advantage of the procedure is pain relief. As patients note, relief comes quickly enough and lasts for a long period. Electrical exposure does not cause addiction. Electrical stimulation can be carried out not only in special rooms, but also at home. Many patients have different devices at their disposal. According to them, using the equipment is quite simple: it is compact and does not require special skills. For many, these devices completely replace drug therapy.

Disadvantages of the procedure
The main disadvantage of the procedure is that it does not eliminate the cause of the pathology. The impact only irritates the muscles, causing them to contract. However, muscle function may not be restored if the neurological damage is severe. Advertising for electrical stimulation devices claims that some of them help. However, there is no clinical evidence of this.
Exposure using professional equipment
Various devices are used to carry out the procedures. One of them is ESMA physiotherapeutic equipment. During the exposure process, not only the fibers are irritated, but also the nerve innervating them with the help of a pulsed current. As a result, a change in bioelectrical activity is observed, spike responses are formed, and intense contraction occurs. During the procedure, the following types of current are used:
- High frequency.
- Pulse.
- Mid-frequency.
- Constant.
- Low frequency.
Mechanism of action
Electrical muscle stimulation is often compared to “gymnastics for the lazy” - the patient does nothing, but his muscles are active. However, experts are in no hurry to draw a direct analogy, since contractions under the influence of current and natural movement are very different. At the same time, one does not replace or cancel the other at all. During ordinary physical activity, regardless of its nature - housework, special exercises, walks, etc. - purposeful work is not carried out by all muscles. Against the background of current exposure, all excited structures are involved. These include smooth and striated fibers. Nerve endings send a signal “up” - to the centers of the brain, and “down” - to organs and systems. At the same time, the walls of large vessels begin to react, and reserve capillary channels open. Due to such massive impact, even the most weakened muscles are prepared for work. However, one should not limit oneself to the use of external influence. To successfully achieve your goal, you need to force your muscles to act.

Equipment types
Electrodes are placed on certain motor points of the hips, back, chest, abdomen, lower limbs. Depending on which model of myostimulator is used, a special conductive gel may be applied to the skin. Usually 15-20 procedures are prescribed per course. The frequency of electrical stimulation is 2-3 times a week. The impact allows you to activate fibers located quite deep, which in normal cases can be difficult to get close to. Electrical stimulation of the lower leg muscles is very effective. As a rule, the effect is aimed at a separate muscle group. In this case, electrical stimulation is performed in a certain sequence. Actually, this determines the positive effect of the procedure. As mentioned above, the equipment is equipped with electrodes. They, in turn, are equipped with devices with the help of which they are attached to the body. The device also has a main unit. It generates a current of a certain strength and frequency. Each muscle group has its own mode of exposure. Often, in addition to the equipment, a special gel or cream is supplied that improves the conductivity of impulses.
Exposure at home
Today, portable devices are quite popular. Some of them are battery operated. However, such devices are only capable of maintaining the state. With reduced tone, for example, there is not much benefit from them, since their power is not enough for a full impact. For example, electrical stimulation of the lower leg muscles with a portable device will relieve fatigue after a working day. However, it will not help correct the condition of the muscles. Among the most common devices, OMRON E4, Enistim-1, ESMA 12.20 COMBI and ESMA 12.48 FAVORITE should be noted.
27263 0
Electrical stimulation is a method of therapeutic treatment with pulsed currents, including intermittent galvanic current, with the aim of stimulating or enhancing the activity of certain organs or systems.
Electrical stimulation of motor nerves and muscles is most often used and successfully developed.
However, electrical stimulation of internal organs is also widely used.
Indications for electrostimulation include the prevention of muscle atrophy, as well as blood clots and embolism during forced inactivity (limb immobilization); reflex atrophy with muscle damage without damage to the motor nerve; peripheral motor neuron paresis (intoxication); expulsion of ureteral stones; weakness of labor, as well as in the postpartum period in order to expel the placenta; fight against atonic bleeding; weakened bowel function; weakened gallbladder function; weakened rectal sphincter function; weakened muscle function Bladder; paresis of the laryngeal muscles; paresis of the facial nerve and facial muscles with flaccid paresis and paralysis; stimulation of the respiratory muscles; obliteration of atherosclerotic vessels; consequences of cerebral palsy; vasospasms; impotence; genital infantilism; obesity; figure correction; peripheral paresis; in order to eliminate the consequences of hypokinesia in athletes; to stimulate reparative osteogenesis, etc.
Before performing electrical stimulation of muscles with impaired innervation, it is necessary to conduct electrodiagnostics (classical and advanced) to establish a diagnosis (taking into account the degree of degeneration of the neuromuscular system) and the possibility of doing so, i.e. determine the optimal parameters of electrical stimulation (type of current, frequency, pulse duration in milliseconds, pause between pulses). These tests are carried out by a doctor.
For moderate and severe degeneration of the neuromuscular system, paresis of the facial seal and facial muscles with flaccid paresis and paralysis, electrical stimulation is a medical procedure.
Electrical stimulation is carried out on the devices “Stimul-1”, “Amp-lipulse-4, 5”, “Neuropulse”, “Diagnostim”, “NET”, “NSitron-626, 627, etc.”, “TUR-RS” , “Stersodnnator”, “Vector-automatic” (see below).
"Stimulus-1" is a source of alternating and rectified sinusoidal current with a frequency of 1-2.5 kHz, used in continuous and pulsed mode (Fig. 95). On the device panel there are: 1 - milliammeter; 2 - signal light for turning on the device in the network; 3 - indicator light for parcel delivery; 4 - potentiometer knob “Patient current”; 5 - button to turn the network on and off; 6 - operating mode switch buttons (continuous and pulse); 7 - buttons for switching types of current - alternating (“Psrsm.”) and rectified (“Ryp.”); 8 - knob for adjusting the duration and cut of bursts.
Rice. 95. Diagram of the control panel of the Stimul-1 device (explanation in the text)
Turning on the device during rhythmic stimulation. 1. The patient should be placed comfortably, electrodes should be applied according to the prescribed technique and securely fixed. 2. Before connecting the wires, make sure that the “Patient Current” knob (4) is moved to the left extreme position and the power button is in the “Off” position. 3. Connect the wires and move the power button to the “On” position, and the signal lamp (2) lights up. Warm up the device for 1-2 minutes.
4. While the device is warming up, set the panel handles according to the prescribed method. Set the mode by pressing one of the buttons (6) (for continuous mode, press the “Continuous” button, for pulse mode, press one of the four buttons indicating the ratio of the duration of bursts and pauses), set the current type switch (7) to the “Alternating” position. or "Exit." The light (3) lights up constantly when the continuous mode is turned on, and goes out during pauses in the pulse mode. When using the pulse mode, set the handle (8) to the extreme left position, and then the bursts will be rectangular in shape, or to the right middle or extreme position, and then the front and cut of the bursts will lengthen, and the current in them will increase gradually.
After setting all parameters of the procedure, turn on the current by turning the “Patient Current” knob (4) from left to right. An increase in current strength is carried out with a glowing lamp (3) until a muscle contraction is obtained. If it is impossible to cause muscle contraction with alternating current, switch to the rectified current mode (“Rectified”), having previously moved the handle (4) to the extreme left position. The sockets for connecting the cable are located on the side of the device, and the red socket on the patient cable will have a positive polarity.
Turning off the device. 1. At the end of the procedure, handle (4) “Patient current” is smoothly moved to the left extreme position until it clicks. In this case, the instrument needle is set to zero, the signal lights go out. 2. The “Network” knob (5) is set to the “Off” position. 3. Remove the wires from the terminals and remove the electrodes.
Technique and general principles of procedures
To carry out electrical stimulation, small (3-8 cm) or large (50-400 cm2) plate electrodes with hydrophilic gaskets, cavity electrodes of a special design, as well as electrodes on a handle with a push-button breaker are used.The choice of electrode depends on the area of influence. Thus, plate electrodes are more often used to stimulate the muscles of a limb or torso. To stimulate the muscles of internal organs, both plate and cavity electrodes are used, and to stimulate the muscles of the face, electrodes on a handle with a push-button breaker are used.
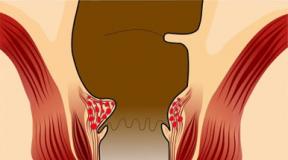
When striated muscles are stimulated, electrodes are placed on certain areas - motor points of nerves or motor muscles (Erb's table). The motor point of a nerve represents the area where the nerve is most superficially located under the skin and accessible to action. The motor point of the muscle represents the place corresponding to the level of entry of the motor nerve into the muscle - the zone of greatest excitability of the muscle. To determine the location of motor points, use the table. Erba.
However, taking into account the variability of their location in each specific case, the physiotherapist determines the location of these points; the first procedure is carried out in his presence. The found motor points are outlined so that during subsequent procedures one does not have to look for them again. When electrically stimulating the muscles of internal organs, the effect is carried out on the projection zone of the organ and on the segmental area, using electrodes large sizes and placing them transversely.
The method of influencing skeletal muscles can be one- or two-polar. With the unipolar (unipolar) technique, one electrode (active) of a small area (4-6 cm2) is placed on the motor point of a muscle or nerve, the second - a larger area (100-150 cm2) - in the region of the corresponding segment along the midline of the body. With the bipolar (bipolar) technique, both electrodes of a small area (4-10 cm2) are placed along the stimulated muscle, one of them is at the motor point, the second is in the distal section in the area of the transition of the muscle to the tendon.
The gasket is moistened with warm tap water, and the electrodes are fixed. The affected part of the body must be in a free and comfortable position so that muscle contraction occurs unhindered and is clearly visible. The current strength is dosed until a clear muscle contraction occurs. Lack of contraction, differential contraction of many muscles at the same time, severe pain indicate that the procedure was performed incorrectly.
In the presence of voluntary muscle contractions, it is advisable to carry out the procedure with the participation of the patient (active electrical stimulation). At the same time, his voluntary movements in a certain rhythm are amplified by an electrical impulse supplied using manual modulation.
Treatment methods
Electrical stimulation of nerves and muscles of the limbs and torso (for flaccid paresis and paralysis, for the prevention of atrophy, thrombus formation during prolonged forced inactivity of the limbs). The impact is carried out using a single-pole (Fig. 96, a, b) or two-pole (Fig. 96, c, d) method.The type of current depends on the state of electrical excitability of the neuromuscular system. With normal excitability and mildly expressed quantitative disorders, diadynamic currents are used (syncopation rhythm; single-cycle, rhythmic, push-pull wave current - “Tone-1”, “Tone-2”), sinusoidal modulated currents in the first mode, the second (PP) type of work with frequency 50-100 Hz, modulation depth 100% with half-cycle duration 2-3 s (“Amplipulse-4, 5”). Apply current until a pronounced muscle contraction occurs. The duration of impact on the muscle is 5-10 minutes. 8-12 procedures are prescribed per course.

Rice. 96. Methods of electrical stimulation: a - unipolar method of stimulation of the right radial nerve; b - unipolar technique of stimulation of the left peroneal nerve; c - bipolar technique for stimulating the flexor carpi ulnaris; d - bipolar method of stimulation of the long peroneal flexor of the right foot
The following pulse mode is used on the “Stimul” device: 10 s - send, 50 s - pause, the total number of cycles in one workout is 10. The maximum tolerated current strength is prescribed, causing maximum contraction of the irritated muscle. Procedures are carried out daily (once or twice a day). 15-20 impacts are applied per course.
In case of a mild partial degeneration reaction (according to electrodiagnostics), exponential pulses are used with a frequency of 80-10 Hz, a pulse duration of 30-12 ms, a pause duration of 2000 ms on the devices “Net”, “Neuropulse”, “Neuroton”, “Diagnostim”.
Single-cycle wave current is used in constant or alternating burst form: period - from 15 to 20 s, leading edge - 3 s, trailing edge - 2 s (“Tone”). Sinusoidal modulated currents are prescribed in the first or second mode, the second type of work (PP), at a frequency of 80 to 10 Hz, modulation depth 100%, pause duration 4-6 s (“Amplipulse”). The current intensity is adjusted until the muscle contracts; the duration of exposure is 3-7 minutes per muscle. Procedures are prescribed daily. The course is 12-20 exposures when using a one- or two-pole technique.
With partial degeneration of the neuromuscular structure of a moderate degree, manual electrical stimulation with an exponential current waveform is possible with a pulse duration of 50-30 ms, a pause duration of 2000 ms on the devices “NET”, “Neuropulse”, “Neuroton”, “Diagnostic”.
In case of partial degeneration of the neuromuscular structure of a severe degree, the doctor performs manual electrical stimulation (unipolar). Optimal parameters of electrical stimulation: exponential current shape, pulse duration - 100-60 ms, pause duration - 2000 ms, current strength is adjusted to muscle contraction, duration of exposure - from 1 to 5 minutes per muscle.
Procedures are most often prescribed twice a day using the NET, Neuropulse, Neuroton, and Diagnostim devices. If the neuromuscular structure is completely degenerated, electrical stimulation is not performed.
Bogolyubov V.M., Vasilyeva M.F., Vorobyov M.G.
Read also...
- Motivational theories. Motive and motivation. Theories of motivation Theories of motivation in various psychological directions
- Purpose of the Phillips School Anxiety Test
- Samara State Regional Academy
- M. V. Koltunova language and business communication. Language and business communication Etiquette and protocol of business communication