Enterprises impact on the environment and people. Industrial production and the environment. The impact of the food industry, mass catering, commerce and trade on the environment
From elementary school we are taught that man and nature are one, that one cannot be separated from the other. We learn about the development of our planet, the features of its structure and structure. These areas influence our well-being: the atmosphere, soil, water of the Earth are, perhaps, the most important components of a normal human life. But why then does environmental pollution go further and larger every year? Let's look at the main environmental issues.
Environmental pollution, which also refers to the natural environment and the biosphere, is an increased content of physical, chemical or biological reagents in it that are not typical for a given environment, brought in from the outside, the presence of which leads to negative consequences.
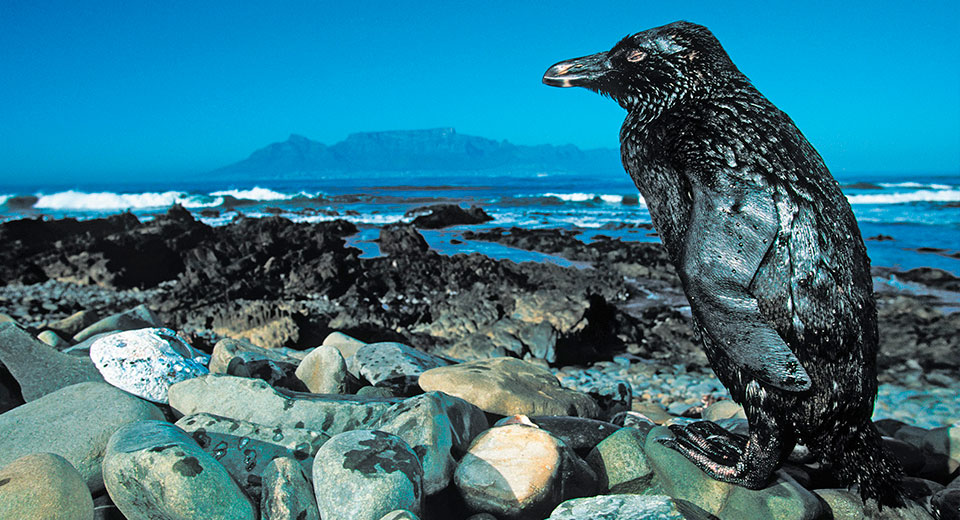

Scientists have been sounding the alarm about an imminent environmental catastrophe for several decades in a row. Conducted research in various fields leads to the conclusion that we are already faced with global changes in climate and external environment under the influence of human activity. Pollution of the oceans due to leaks of oil and petroleum products, as well as garbage, has reached enormous proportions, which affects the decline in populations of many animal species and the ecosystem as a whole. The growing number of cars every year leads to large emissions into the atmosphere, which, in turn, leads to drying of the earth, heavy rainfall on the continents, and a decrease in the amount of oxygen in the air. Some countries are already forced to bring in water and even buy canned air because production has ruined the country's environment. Many people have already realized the danger and are very sensitive to negative changes in nature and major environmental problems, but we still perceive the possibility of a disaster as something unrealistic and distant. Is this really so or is the threat imminent and something needs to be done immediately - let's find out.
Types and main sources of environmental pollution
The main types of pollution are classified by the sources of environmental pollution themselves:
- biological;
- chemical
- physical;
- mechanical.
In the first case, environmental pollutants are the activities of living organisms or anthropogenic factors. In the second case, the natural chemical composition of the contaminated sphere is changed by adding other chemicals to it. In the third case, the physical characteristics of the environment change. These types of pollution include thermal, radiation, noise and other types of radiation. The latter type of pollution is also associated with human activity and waste emissions into the biosphere.
All types of pollution can be present either separately on their own, flow from one to another or exist together. Let's consider how they affect individual areas of the biosphere.
People who have traveled a long way in the desert will probably be able to name the price of every drop of water. Although most likely these drops will be priceless, because human life depends on them. IN ordinary life, we, alas, do not attach such great importance to water, since we have a lot of it and it is available at any time. But in the long term this is not entirely true. In percentage terms, only 3% of the world's fresh water remains unpolluted. Understanding the importance of water for people does not prevent people from polluting an important source of life with oil and petroleum products, heavy metals, radioactive substances, inorganic pollution, sewage and synthetic fertilizers.
Contaminated water contains a large amount of xenobiotics - substances foreign to the human or animal body. If such water enters the food chain, it can cause serious food poisoning and even death for everyone in the chain. Of course, they are also contained in products of volcanic activity, which pollute water even without human help, but the activities of the metallurgical industry and chemical plants are of predominant importance.
With the advent of nuclear research, quite significant harm has been caused to nature in all areas, including water. Charged particles that get into it cause great harm to living organisms and contribute to the development of cancer. Wastewater from factories, ships with nuclear reactors, and simply rain or snow in the nuclear testing area can lead to contamination of water with decomposition products.
Sewage, which carries a lot of garbage: detergents, food debris, small household waste and more, in turn contributes to the proliferation of other pathogenic organisms, which, when entering the human body, give rise to a number of diseases, such as typhoid fever, dysentery and others.
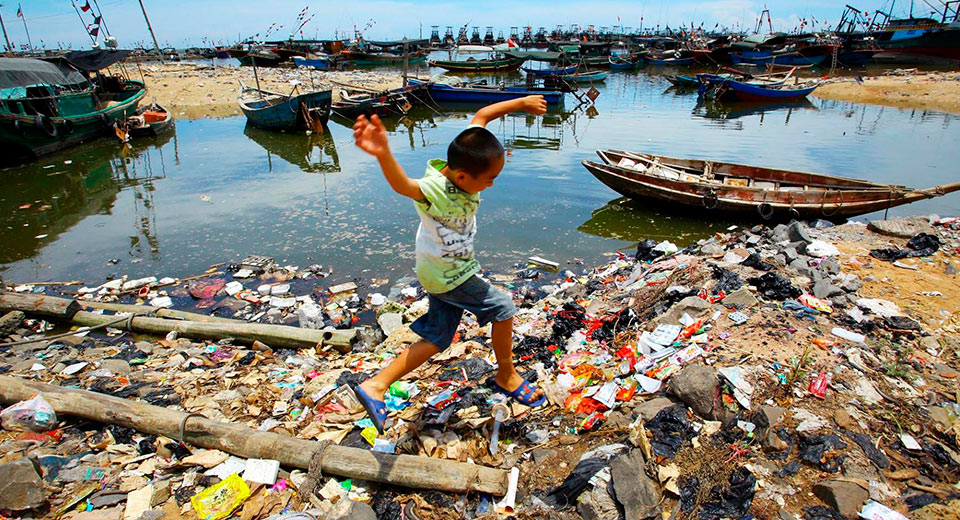

It probably doesn’t make sense to explain how soil is an important part of human life. Most of the food that humans eat comes from the soil: from cereals to rare types of fruits and vegetables. In order for this to continue, it is necessary to maintain the condition of the soil at the proper level for the normal water cycle. But anthropogenic pollution has already led to the fact that 27% of the planet's land is susceptible to erosion.
Soil pollution is the ingress of toxic chemicals and debris into it in high quantities, interfering with the normal circulation of soil systems. Main sources of soil pollution:
- residential buildings;
- industrial enterprises;
- transport;
- Agriculture;
- nuclear power.
In the first case, soil pollution occurs due to ordinary garbage that is thrown in the wrong places. But the main reason should be called landfills. Burned waste leads to contamination of large areas, and combustion products spoil the soil irrevocably, polluting the entire environment.
Industrial enterprises emit many toxic substances, heavy metals and chemical compounds that affect not only the soil, but also the life of living organisms. It is this source of pollution that leads to technogenic soil pollution.
Transport emissions of hydrocarbons, methane and lead, entering the soil, affect food chains - they enter the human body through food.
Excessive plowing of the land, pesticides, pesticides and fertilizers, which contain enough mercury and heavy metals, lead to significant soil erosion and desertification. Abundant irrigation also cannot be called a positive factor, since it leads to soil salinization.
Today, up to 98% of radioactive waste from nuclear power plants, mainly uranium fission products, is buried in the ground, which leads to degradation and depletion of land resources.

The atmosphere in the form of a gaseous shell of the Earth is of great value because it protects the planet from cosmic radiation, affects the relief, determines the Earth's climate and its thermal background. It cannot be said that the composition of the atmosphere was homogeneous and only began to change with the advent of man. But it was precisely after the start of active human activity that the heterogeneous composition was “enriched” with dangerous impurities.
The main pollutants in this case are chemical plants, the fuel and energy complex, agriculture and cars. They lead to the appearance of copper, mercury, and other metals in the air. Of course, air pollution is felt the most in industrial areas.
Thermal power plants bring light and heat to our homes, however, at the same time they emit huge amounts of carbon dioxide and soot into the atmosphere.
Acid rain is caused by waste released from chemical plants, such as sulfur oxide or nitrogen oxide. These oxides can react with other elements of the biosphere, which contributes to the emergence of more harmful compounds.
Modern cars are quite good in design and technical specifications, but the problem with the atmosphere has still not been solved. Ash and fuel processing products not only spoil the atmosphere of cities, but also settle on the soil and lead to its deterioration.
In many industrial and industrial areas, use has become an integral part of life precisely because of environmental pollution from factories and transport. Therefore, if you are concerned about the state of the air in your apartment, with the help of a breather you can create a healthy microclimate at home, which, unfortunately, does not eliminate the problems of environmental pollution, but at least allows you to protect yourself and your loved ones.

Industrial enterprises benefit the economies of many countries, but cause harm to the environment. Today, production in the following areas has a negative impact on the environment:
- metallurgical;
- petrochemical;
- mechanical engineering;
- chemical.
As a result of the operation of these facilities, carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide gases, ash and toxic gases are released into the atmosphere. These elements, first of all, pollute the atmosphere, as well as soil and water, and affect flora and fauna.
Pollution from metallurgical plants
Experts believe that among all enterprises, the most pollution comes from ferrous and non-ferrous metallurgy plants. As a result of their activities, harmful substances are released into the air. Metallurgical enterprises discharge large amounts of wastewater into water bodies. To reduce the negative impact of factories on the environment, they need treatment facilities. The old ones need to be replaced with new ones and used to their full capacity.
Chemical pollution
Chemical plants, as their name suggests, cause direct damage to the environment. In the process of work, rubber, various acids, dyes, polymers and other substances are used. They release harmful elements that are released into the atmosphere and washed off with water. During the production of some chemicals and materials, not only synthetic resources are used, but also natural ones. When interacting, natural raw materials become contaminated with other substances.
Chemical and petrochemical enterprises release the following substances into the environment:
- nitrogen oxides;
- carbon dioxide;
- sulfur dioxide;
- various gases.
Surface waters are polluted with formaldehydes and phenols, methanol and various heavy metals, chlorides and nitrogen, benzene and hydrogen sulfide.
Results of environmental pollution by industrial enterprises
While working, industrial enterprises produce a lot of useful products, ranging from dishes and household utensils to cars, ships and airplanes. To manufacture certain items, a large amount of resources is required. During their processing, a large amount of waste appears. They need to be carefully reconsidered, since some of them can be recycled. Using a rational approach to environmental management, it is possible to significantly reduce environmental pollution from industrial enterprises.
They belong to points of high danger of environmental pollution with toxic substances. During the operation of many of them, hazardous substances are released into the environment. The volumes of these emissions, compared, for example, with waste from the mining industry, are relatively small, but can cause significant harm to the environment. Many wastes are toxic, making their storage a problem. At dump sites there are huge masses of various processing residues, which continue to cause colossal harm to the environment. During the processes of water and wind erosion, hazardous substances enter the atmosphere, water and soil.
Note 1
The danger of chemical industry enterprises as sources of environmental pollution in our country is determined not only by the amount of substances emitted during normal production conditions, but also by uncontrolled releases of toxic substances during accidents.
The main toxic wastes and emissions from chemical industry enterprises are presented:
Finished works on a similar topic
- Coursework 410 rub.
- Essay Impact of chemical industry enterprises on the environment 240 rub.
- Test Impact of chemical industry enterprises on the environment 190 rub.
- organic solvents,
- amines,
- aldehydes,
- chlorine and its derivatives,
- nitrogen oxides,
- hydrogen cyanide,
- fluorides,
- sulfur compounds (sulfur dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, carbon disulfide),
- organometallic compounds,
- phosphorus compounds,
- mercury
- etc.
Emissions of harmful substances into the atmosphere increase if chemical-technological equipment is placed in open areas, its tightness is not strict, and there are a large number of external technological communications. The temperature of gaseous emissions from many chemical industry plants differs little from the temperature of the surrounding atmospheric environment, resulting in the effect of accumulation of toxic substances near emission sources.
The wastewater of most chemical enterprises is oversaturated with a variety of toxicants. Along with the substances emitted by these enterprises into the air, wastewater from chemical industries also contains other very dangerous compounds - organic substances, mineral acids in various concentrations, up to concentrated ones, soluble metal salts, silica, etc.
Note 2
The most dangerous chemical industries for the environment and humans include ore beneficiation processes, coke and petrochemical production, enterprises for the production of various fertilizers, acids, pulp and paper industry facilities, artificial fiber plants, and many others, i.e. almost the entire spectrum of modern chemical technology.
Ways to reduce the harmful impact of chemical industry enterprises on the environment
The main ways to reduce the harmful impact of chemical industry enterprises on the environment are to save natural resources during production, organize recycled water supply, waste-free production schemes, better purification of emissions and wastewater using modern technologies and recycling of captured pollutants that can be reused in the economy . At the same time, pollution of rivers and reservoirs with toxic compounds is prevented. Unfortunately, only a small proportion of waste from large industrial plants is currently recycled.
Note 3
Legislation has introduced more or less justified requirements in terms of minimizing discharges by enterprises and recycling hazardous waste in order to ensure an adequate level of safety in the chemical industry. However, in practice, these schemes require a radical re-equipment of enterprises and the use of expensive technologies.
Most enterprises either simply do not have the funds to implement environmentally friendly technologies, or, even if such funds are available, enterprises do not implement them due to a decrease in profits at the refurbishment stage, the maximization of which is their main goal. In this regard, only a small number of large enterprises use environmentally friendly technologies; other facilities continue to operate as before.
INTERACTION OF THE ENTERPRISE WITH THE ENVIRONMENT
Environmental passport of the enterprise is a comprehensive document containing characteristics of the relationship between an enterprise and the environment. The environmental passport contains general information about the enterprise, the raw materials used, writing technological schemes for the production of main types of products, schemes for treating wastewater and air emissions, their characteristics after treatment, data on solid and other waste, as well as information on the availability in the world of technologies that ensure the achievement of the best specific indicators for environmental protection . The second part of the passport contains a list of planned activities aimed at reducing the burden on the environment, indicating the timing, costs, specific and total volumes of emissions of harmful substances before and after the implementation of each activity.
Indicators of the enterprise’s impact on the environment:
1. Environmental friendliness of manufactured products.
2. Impact on water resources.
3. Impact on air resources.
4. Impact on material resources and production waste.
5. Impact on land resources
IMPACT OF ENTERPRISES ON THE ENVIRONMENT
METALLURGICAL ENTERPRISE
A modern metallurgical enterprise for the production of ferrous materials has the following main stages: production of pellets and agglomerates, coke, blast furnace, steelmaking and rolling production. The enterprises also include ferroalloy, refractory and foundry production. All of them are sources of air and water pollution.
All metallurgical processes are sources of pollution with dust, carbon oxides and sulfur.
Ferrous metallurgy enterprises account for 15-20% of total industrial atmospheric pollution, which amounts to more than 10.3 million tons of harmful substances per year, and in areas where large metallurgical plants are located - up to 50%. On average, per 1 million tons of annual productivity Ferrous metallurgy plants produce dust emissions of 350, carbon monoxide 400, nitrogen oxide - 42 tons/day. Ferrous metallurgy is one of the largest consumers of water. Water consumption accounts for 12-15% of total water consumption by industrial enterprises in the country. 49% of water is used for equipment cooling, gas and air purification - 26, hydrotransport -11, metal processing and finishing - 12, other processes - 2% of water.
ENERGY ENTERPRISE
The interaction of an energy enterprise with the environment occurs at all stages of production and use of fuel, transformation and transmission of energy. A thermal power plant actively consumes air.
One of the factors affecting the environment from coal-fired thermal power plants is emissions from fuel storage, transportation, dust preparation and ash removal systems. During transportation and storage, not only dust pollution is possible, but also the release of fuel oxidation products. Removal of slag and ash has different impacts on the environment. The main factors of the impact of thermal power plants on the hydrosphere are heat emissions, which can result in: a constant local increase in temperature in the reservoir; temporary increase in temperature; changes in freeze-up conditions and winter hydrological regime; changing flood conditions; changes in the distribution of precipitation, evaporation, fog.
During normal operation, nuclear power plants produce significantly less harmful emissions into the atmosphere than thermal power plants running on fossil fuels. Thus, the operation of a nuclear power plant does not affect the content of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and does not change its chemical state. The greatest danger is posed by nuclear power plant accidents and the uncontrolled spread of radiation. Therefore, NPP projects must guarantee sulfur to ensure the nuclear safety of the environment in the event of any possible single violation of any NPP system.
Hydroelectric power plants (HPPs) also have a significant impact on the natural environment, which manifests itself both during construction and during operation. The construction of reservoirs in front of a hydroelectric power station dam leads to flooding of a large adjacent area and affects the coastal topography in the area of hydroelectric power station construction, especially when it is built on lowland rivers. Changes in the hydrological regime and flooding of territories cause changes in hydrochemical and hydrological regimes water masses. With intense evaporation of moisture from the surface of reservoirs, local climate changes are possible: increased air humidity, formation of fogs, increased winds, etc.
MACHINERY ENGINEERING ENTERPRISE
Of the large volume of industrial emissions that enter the environment, mechanical engineering accounts for only a small part of it, 2%.
However, machine-building enterprises have basic and supporting technological production processes with a very high level of environmental pollution. These include: -in-plant energy production and other processes associated with fuel combustion; -Foundry; -metalworking of structures and individual parts; -welding production; -galvanic production; - paint and varnish production. In terms of the level of environmental pollution, the areas of electroplating and dyeing shops of both mechanical engineering in general and defense enterprises are comparable to such major sources of environmental hazard as the chemical industry; foundry is comparable to metallurgy; territories of factory boiler houses - with areas of thermal power plants, which are among the main polluters. Thus, the engineering complex as a whole and the production of defense industries, as its integral part, are potential pollutants of the environment: - airspace; -surface water sources; -soil.
http://tqm.stankin.ru/arch/n02/zasedanie3/index38.htm
Well-established production is important for the development of countries. But the impact of factories on the environment is negative. Emissions of gases into the air, runoff into water bodies, landfills - this pollutes the environment, making it uninhabitable.
Industries
The entire industry is divided into mining and processing. The latter is divided into heavy and light.
Extractive industries:
- Mining: oil, gas, ore, metals, mining chemical raw materials, diamonds, salt
- Wood removal
- Hunting, fishing
- Hydroelectric power stations
After extraction, processing begins. Heavy industries:
- Metallurgy
- Mechanical engineering
- Fuel production
Light industry includes the production of:
- Fabrics
- Shoes
- Jewelry
- Toys
- Dyes, etc.
The consequences of any production are waste of varying degrees of harmfulness.
Classification and impact of waste
Factory waste is divided into returnable, secondary and irrecoverable.
Returnable waste can be reused if the requirements for the product, its composition, or material shortages change. Sawdust is used as fuel, in repairs and agriculture. In the dairy industry, this is whey, skim milk.
Recyclable waste is processed and disposed of, and used in other areas. Melting of metals, production of technical glass.
Irrevocable waste is not suitable for recycling or disposal. They pollute the environment: they are burned, buried (or simply left in landfills), and dumped into water bodies. Wastewater containing petroleum products, salts, hydrogen sulfide, emissions into the atmosphere.
The bulk of pollutants:
- Various gases (oxides of sulfur, nitrogen, carbon)
- Heavy metals
- Oil and petroleum products
- Plastics
- Organic compounds
- Rubber
According to the area of influence, pollutants are divided into atmospheric, hydrosphere and lithospheric.
Atmospheric pollutants are divided into primary – they immediately enter the air, and secondary – the result of the transfer of primary pollutants.
The main sources of negative impact on the environmental situation are machine-building enterprises, oil, metallurgical, and chemical enterprises. In mechanical engineering, acids, salts of heavy metals, alkalis, and cyanides are used. During the operation of oil refineries, phenol, hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, sulfur dioxide, etc. are released into the atmosphere.

The fashion industry and agricultural production also have an impact on the environment.
Over the past 10 years, clothing production has doubled. Fashion changes, needs grow, and with them the volume of clothing production, waste, and the number of discarded items.
A significant part of clothing is made from polyester - it does not wrinkle, retains color and does not wear out for a long time. But it takes hundreds of years to decompose.
The starting materials for producing polyester are oil and gas (hydrocarbons).
Destruction natural fibers also poses a danger - linen and cotton fabrics contain modal, lyocell, and viscose. As these tissues decompose, methane is released.
A common fiber in textile production is cotton.

The advantage of cotton over polyester is that during its processing, carbon dioxide is released several times less. But when growing cotton, a large number of harmful chemicals are used - pesticides, which are also used in agriculture. This reduces the value of products and disrupts the natural environment of soil and water. Insects and microorganisms become resistant to chemicals, forcing the use of more toxic substances. When pesticides enter the human body, they disrupt the functioning of the central nervous system. nervous system, can cause cancer and decreased immunity.
By saving on waste processing and disposal, a person primarily harms himself.
Every year more than 70 tons of toxic salts rise from the water.
Sulfur dioxide, once released into the atmosphere, is oxidized to sulfuric anhydride, the latter reacts with water vapor and forms droplets of sulfuric acid.
Sulfur dioxide forms acid rain, which causes diseases in the population and affects animals and plants.
Flora does not grow on contaminated soil, which leads to the extinction of animals.
How to reduce environmental damage to industry
How can you reduce the negative impact of industrial enterprises on the environment:
- Monitoring the environmental situation. In Germany, there is a set of laws “Crimes against the environment”, spelled out in the Criminal Code. Violation of laws is punishable by imprisonment from 3 to 10 years. In the USA, violation of the law on water, soil and air quality can result in a fine of up to 25 thousand dollars and imprisonment for up to 2 years. In China, the government has the right to fine factories. Japan has a Basic Law on Pollution Control. An environmental assessment and monitoring of the quality of water bodies, atmosphere, and land are carried out.
- Recycling and safe disposal of waste. Application of modern technologies that reduce the amount and danger of emissions
- Financial incentives and benefits for factories with the least harmful impact on the environment. Thus, the Efes Rus brewery in Vladivostok has been using new treatment facilities since 2016; according to management, investments amounted to 280 million rubles. Gazprom Neft launched the Biosphere treatment facility at the Moscow oil refinery in Omsk.
- Financing activities aimed at improving the environmental situation - waste collection and subsequent disposal, soil restoration, growing trees, etc. Greenpeace in Russia has been carrying out the “Reviving Our Forest” project for more than 16 years. In Tuapse, KubanEcoPlus LLC has installed modern system cleaning. JSC Okos is engaged in water purification in Zelenogradsk, Svetlogorsk and Pioneer.
Every year, the Center for Environmental Policy and Law at Yale University compiles environmental ratings of countries. The degree of environmental pollution and the rational use of natural resources are assessed. For 2018, Switzerland, France and Denmark took 1st to 3rd place, respectively. Russia is in 52nd place out of 180.
Only about 50% of industrial enterprises in Russia have modern treatment technologies.
To reduce the negative impact of factories on the environment, it is necessary to strengthen control over the extraction of mineral resources and carry out measures to clean up and restore the environment. Tighten penalties for excess harm and savings on wastewater treatment plants, produce alternative energies– wind generators, solar panels, hydroelectric generators.