Blockage of blood vessels in the brain, symptoms and treatment. Blockage of blood vessels: causes, symptoms and methods of treatment What leads to blockage of arteries
Shoshina Vera Nikolaevna
Therapist, education: Northern Medical University. Work experience 10 years.
Articles written
The brain is the most important organ that is responsible for the functioning of the entire organism as a whole, and, consequently, for the full functioning of a person - performance, intellectual potential and mental abilities. Damage to its tissues as a result of any pathology can lead to serious consequences. This is why it is so important that the vessels responsible for blood supply, delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the brain are healthy and have good throughput.
How it happensprocess
The supply of nutrients to the brain necessary for its normal functioning is disrupted if the capacity of blood vessels is reduced due to their narrowing, blockage or obstruction. Why do vascular pathologies occur?
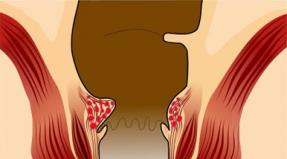
Blood vessels are the most important part of the human body. They are a component of the circulatory system, which ensures the functioning of all organs. It’s hard to believe, but the total length of the vessels, neatly distributed throughout the body and covering all its corners without exception, is 100,000 kilometers! The regulator of blood movement through the vessels is the heart, which acts as a kind of pump.
What is a blood vessel? This is an elastic tube through which blood circulates. Vessels cover the human body with a dense dense network, uniting into systems. In order for blood to flow freely through all systems, the required pressure is maintained inside the tubes. The strength of the tubes is due to the complex structure of the vessels, which have three layers. Each layer performs a specific function:
- Interior. It consists of thin epithelium, which provides reliable protection of blood components from pathologically harmful enzymes and the smoothness of the surface of the vascular walls.
- Average. Consists of muscle, collagen and elastic tissues and fibers. Responsible for the strength and elasticity of the walls of blood vessels, so that blood does not go beyond their boundaries.
- Outer. It is a loose fabric consisting of a connective fibrous texture. It is this tissue that protects blood vessels from the effects of provoking factors.
For a number of reasons, cholesterol plaques begin to accumulate in the inner layer of blood vessels, which interfere with the free flow of blood. In this regard, circulation decreases, vascular walls lose elasticity. This leads to damage to blood vessels.
Unfortunately, today cerebral vascular pathologies are not considered a rare phenomenon. And if previously older people suffered from them, today they are also diagnosed in representatives of the younger generation.
Causes
There are a number of factors that provoke the development of cerebral vascular obstruction. Here are the most common ones:
- Physical inactivity. Low physical activity and sedentary work lead to disruption of circulation and free flow of blood through the vessels.
- Passion for unhealthy and unhealthy foods (fatty, salty, fast food, etc.) containing high amounts of fats and carbohydrates. Such food provokes the deposition of plaques and toxins, which over time clog the blood vessels.
- Bad habits. Drugs, alcohol, and narcotic substances contribute to blood thickening and increase the risk of thrombosis. Clogged vessels become sluggish, lose elasticity, and plaques form on them.
- Insufficient water intake. Violation of the drinking regime increases blood viscosity, which impedes normal blood flow.
- A state of constant stress, emotions both negative and positive.
- Genetic predisposition may pose a certain risk of developing pathologies of the cerebral blood supply system.
- Varicose veins, thrombophlebitis, poor blood clotting.
- Some diseases ( diabetes, autoimmune changes in blood vessels).
- Skull injuries, bruises of brain tissue, post-traumatic complications, which are characterized by filling the lumens of arteries and veins with fat particles.
- Metabolic disorders, obesity.
- Pregnancy. During pregnancy, the level of blood clotting may increase.
- Release of large amounts of toxic substances leading to blood thickening (crash syndrome).
- Taking certain medications, one of them side effects which is the formation of blood clots and vascular embolism.
It can also be caused by air ingress due to unprofessional medical procedures - injections, IVs.
Types ofatologistii and ssymptoms
Blockage of cerebral vessels (occlusion, embolism, thromboembolism) is a dangerous syndrome that occurs due to the fact that blood clots, detached from the site of their formation, enter the circulating blood and clog the lumens of blood vessels.
Thromboembolism causes serious disruption of the flow of blood and cerebral cells. This can lead to very dangerous consequences - encephalopathy, necrosis, heart attack, stroke and other pathologies.

There are two types of cerebral vascular occlusions:
- Arterial (with impaired blood flow). It is characterized by rapid development and closure of the lumen in the arterial bed. In medical practice it occurs quite often and ends in 40% of cases. That is why urgent response and immediate treatment are necessary.
- (changes in blood flow). It develops gradually and occurs due to obstruction of the venous lumen.
Embolism of cerebral vessels is characterized by certain symptoms, among which the main one is of a pressing or bursting nature. At the same time, the pain is resistant to analgesics, and it is very difficult to relieve the pain syndrome. With venous thrombosis, the pain is periodic, over time it becomes more and more common, and the intensity increases.
Additional signs to suspect embolism in a patient include:
- Frequent fainting, loss of consciousness.
- Loss of performance, fatigue, drowsiness, weakness.
- Disorientation in space, impaired consciousness.
- Hypertension.
- Paleness of the skin.
- Hyperthermia.
- Convulsions, epileptic conditions.
- Cardiac arrhythmia, rapid heartbeat.
- Depression, feeling of fear.
- Rigidity of the neck muscles and others.
- Deterioration of visual function (split objects, blurred vision).
- Change in pressure. With arterial occlusion it increases, with venous occlusion it decreases.
- Speech disturbances (if the lesion has become).
- Deafness in the ears (with pathology of the temporal lobe).
At the initial stage, the symptoms are vague, but as the disease develops, the signs become more pronounced.
At the first stage, the patient feels fatigue, his attention decreases, his memory deteriorates, and headaches appear. Many patients attribute this condition to severe fatigue Therefore, they do not pay special attention to these symptoms. Meanwhile, the sooner a person seeks help from a medical institution, the higher the chances of a successful outcome.
The second stage is characterized by deterioration of the condition. Headaches become more and more debilitating, turning into long-lasting headaches. The patient experiences tinnitus and fainting. Appetite decreases, attention is distracted, coordination of movements and sensitivity of the limbs deteriorate. In some cases, there may be a false urge to urinate.

The third stage no longer raises doubts about diseases associated with blockage of blood vessels, because the signs appear with all intensity. In addition, the patient experiences obvious mental retardation, poor coordination, problems with movement, and uncontrolled urination and defecation. At this stage, a person, as a rule, can no longer take care of himself and control his actions, so he needs the help of loved ones.
What to do if you suspect
If there is serious concern that the patient has an embolism, the first thing to do is to lay him down, placing a pillow under his head and shoulders, and prohibit him from moving. If this is not done, the patient may experience an ischemic stroke.
After conducting the necessary diagnostic tests and making a diagnosis, the doctor prescribes treatment. At the same time, he must take into account individual characteristics patient, concomitant diseases, age.
However, as you know, any disease is easier to prevent than to treat. This also applies to blockage of blood vessels in the brain, which does not occur just like that, but is a consequence of pathologies already existing in the body.
The simplest preventive measures are giving up bad habits, promoting a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition and reasonable physical activity. And, of course, we must not forget about systematic medical examinations, which will help to timely identify diseases such as cerebral embolism.
The performance, intelligence, and mental activity of a person depend on the condition of the blood vessels. Blockage of blood vessels in the brain is accompanied by deterioration of blood circulation in the brain, insufficient oxygen supply and useful substances, which can lead to serious consequences in the future.
What is the danger of blockage of blood vessels?
Blockage of blood vessels in the brain caused by the accumulation of air bubbles, fat, or a blood clot is called an embolism.. Penetrating into arteries with a narrow lumen, the particles provoke their blockage, disrupting blood flow and causing tissue destruction from lack of oxygen.
If left untreated, the pathology can cause:
- cerebral infarction;
- thrombus formation;
- cerebral hemorrhage;
- dementia.
The pathology is most often observed in the elderly, but it can also occur in young people under the influence of unfavorable factors.
Symptoms
The cerebral circulatory disorder is initially asymptomatic. However, there are some signals indicating the development of pathology.
 To general symptoms vascular diseases can be attributed:
To general symptoms vascular diseases can be attributed:
- tendency to frequent dizziness and fainting;
- sleep disorder;
- headaches, migraine attacks;
- memory impairment;
- fatigue;
- numbness of hands and feet;
- deterioration of coordination;
- mood variability.
After this, other signs may be added:
- gait disturbance: the person may shuffle or mince;
- noise in ears;
- visual impairment;
- prolonged migraines;
- false need to urinate.
Lack of therapy leads to progression of the disease and the appearance of new symptoms:
- noticeable loss of coordination of movements;
- deterioration of intellectual abilities;
- various disorders of the urinary system.
Severe cases of arterial blockage often result in complete immobility and death..
In the advanced stage, systematic medical care is required: the patient may lose control of his actions and become incapacitated.
Causes
 Chronic blockage of the lumen of blood vessels, impeding blood flow, can occur as a result of injuries, atherosclerosis, as well as various diseases: diabetes, high blood pressure, vasculitis.
Chronic blockage of the lumen of blood vessels, impeding blood flow, can occur as a result of injuries, atherosclerosis, as well as various diseases: diabetes, high blood pressure, vasculitis.
Other reasons for the development of pathology include:
- lack of physical activity;
- genetic predisposition;
- chronic stress;
- negative habits: excessive drinking, smoking;
- poor nutrition.
Eating fatty foods and foods containing additives leads to the accumulation of cholesterol in the arteries, which, in turn, is a prerequisite for the development of atherosclerosis.
Diagnostics
 A neurologist will help identify the pathology, who will evaluate the neurological symptoms, mental abilities of the patient, as well as the degree of manifestation of reflexes. However, to make an accurate diagnosis, the following studies will be required:
A neurologist will help identify the pathology, who will evaluate the neurological symptoms, mental abilities of the patient, as well as the degree of manifestation of reflexes. However, to make an accurate diagnosis, the following studies will be required:
- ultrasound diagnostics;
- computed tomography;
- angiography;
- electroencephalography.
These methods will help determine the condition of the brain, the size and location of lesions and the nature of the disease.
Treatment
Treatment of the disease depends on clinical picture and forms of pathology. In case of exacerbation, the use of medications will be required to help reduce symptoms and improve cerebral circulation.
Most often, an integrated approach is used, including the use of medications, adjustments to diet and lifestyle, as well as alternative medicine recipes. Some cases require surgery.
Medicines
 The most commonly used drugs are:
The most commonly used drugs are:
- statins - medications that reduce cholesterol production, for example, simvastatin, zocor;
- fibrates – medications that prevent atherosclerotic plaques, lipanor, fenofibrate;
- papaverine and aminophylline are used to dilate cerebral blood vessels;
- to strengthen immune system, prescribe antioxidants and vitamin-mineral complexes;
- Cavinton and Vasobral are used to improve blood circulation in the brain.
The duration and dose of medication use is determined by the attending physician. In some cases, the patient has to take medications for the rest of his life.
However, no medicine will have the desired effect without following a balanced diet.
- exclude animal fats and smoked meats;
- give up fried foods, spicy salty food, fast food;
- limit the consumption of sweets and soda;
- enrich the diet with vegetables, fruits, and seafood.
In addition, you need to monitor your body weight, give up negative habits, walk more often and exercise.
ethnoscience
You can clear arteries of harmful deposits using folk remedies. Home remedies for blockage treatment are used as adjuvant therapy..
In acute or advanced stages of the disease, alternative medicine may become useless.
Rose hip
Rosehip infusion showed excellent results in eliminating vascular obstruction in the brain. To prepare, you will need to leave 50 g of fruit for 6 hours. Take a decoction of 200 g, several times a day, for a month.
Hawthorn
The fruits are poured into 500 g of boiling water, boiled, honey is added to the drink and consumed 20 g before meals, twice a day.
 Given folk remedy promotes the removal of cholesterol plaques from the arteries and strengthens the walls.
Given folk remedy promotes the removal of cholesterol plaques from the arteries and strengthens the walls.
To prepare, you will need 200 g of nut partitions and the same amount of vodka.
The infusion is kept for 14 days in a dark place.
Take 20 drops of the product, diluting it with 50 g of water, three times a day, for half a month.
Sea buckthorn oil
Daily consumption of 1 teaspoon of oil before meals will help improve the health of the blood vessels in the head. The course of therapy is 21 days. After a break of 1 month, treatment is repeated.
Garlic
 Garlic is an excellent natural remedy for preventing colds. Beneficial features allow it to be used to cleanse vascular walls from cholesterol:
Garlic is an excellent natural remedy for preventing colds. Beneficial features allow it to be used to cleanse vascular walls from cholesterol:
- To prepare, several cloves of garlic are crushed in a meat grinder, poured with alcohol and left in a dark place for 10 days. Strain the composition and take 20 drops, diluted with 100 g of water, half an hour before meals, three times a day. The course of treatment is 30 days. This remedy will help cleanse the arteries and remove cholesterol deposits.
- Peeled heads of garlic are placed in 200 g of milk. The mixture is boiled until the garlic softens. The milk is drained and taken 1 tablespoon three times a day.
- The following recipe will help to effectively cleanse the vascular walls. To prepare, you will need 1 head of garlic and 1 lemon in peel. The ingredients are ground in a meat grinder, poured into 1 liter of water, infused and consumed 50 g three times a day for 1 month. The course of therapy is twice a year. This remedy will help stabilize blood pressure and strengthen the immune system.
Drinking freshly squeezed juices from celery, tomato, carrots and pomegranate will be beneficial for blood vessels.
To prevent blockage of blood vessels, it is necessary to observe healthy image life, eat rationally, do not neglect regular physical activity, and also systematically undergo a medical examination. This is especially true for people at risk.
Blockage of cerebral vessels is a pathological process in which the blood supply to the brain is disrupted. In pathology, disturbances in the functioning of various organs and systems are diagnosed, therefore, if pathology occurs, it is recommended to treat it in a timely manner.
Cerebral embolism appears in patients when exposed to a number of provoking factors:
- Drinking insufficient water. If the drinking regime is violated, the viscosity of the blood increases. This leads to disruption of normal blood flow.
- Genetic predisposition. People whose relatives suffered from the disease are at risk.

- Stressful situations. With the constant experience of positive and negative emotions, patients develop illness.
- Bad habits. When the body is exposed to nicotine, alcohol and drugs, a person’s blood thickens, which leads to an increased risk of thrombosis. When blood vessels become clogged, they become sluggish, lose elasticity, and form plaques.
- Predominance in the diet of foods that contain fats and carbohydrates in large quantities. With improper nutrition, waste appears in the blood, and plaques appear on the walls of blood vessels.
- Physical inactivity. With insufficient physical activity and a sedentary lifestyle, circulation and free flow of blood through the vessels are disrupted.

Pathology is diagnosed for a variety of diseases. People who suffer from varicose veins are at risk. The disease develops in patients with thrombophlebitis. Insufficiency of blood coagulation function becomes the cause of pathology. The cause of the disease is atherosclerosis. The likelihood of developing the disease increases in people with diabetes mellitus or autoimmune vascular changes.
With obesity and impaired metabolism, patients are diagnosed with the disease. During pregnancy, there may be an increase in the level of blood clotting, which leads to illness. It develops if a large amount of substances is released in the patient's body, which leads to blood thickening. If a person takes certain medications, this leads to pathology.

Blockage of blood vessels in the brain is observed during diseases in the human body and exposure to various provoking environmental factors.
Types and symptoms of the disease
With thromboembolism, which affects the brain, blood clots break away from the site of their formation and clog the lumen of the blood vessels. In pathology, the occurrence of oxygen starvation of cerebral cells is diagnosed. Embolization can be arterial or venous.
The first is characterized by rapid development and blocks the lumen in the brain. Without immediate treatment, patients experience ischemic stroke. Venous embolism develops gradually and closes the gaps in the veins.

The main symptom of the disease is headache, which has a pressing or bursting character. The pain cannot be relieved with analgesics. The venous form of the disease is accompanied by periodic pain.
The pathological process is accompanied by additional symptoms: hypertension, fainting, impaired consciousness, disorientation in space, drowsiness, loss of consciousness.
When sick, the patient is diagnosed with weakness and excessive fatigue even when performing usual activities. If the disease develops in the temporal lobe, it is accompanied by tinnitus and deafness. When the frontal lobe is damaged, patients have speech impairment.

When examining the patient, abnormalities in blood pressure are diagnosed. If a person has an arterial form of the disease, then this leads to an increase in it, and if it is venous, then a decrease. Cerebral embolism is accompanied by deterioration of visual function.
Patients report double vision and visual impairment. Symptoms of the disease are depression and a feeling of fear.

With cerebral embolism, the development of meningeal symptoms in the form of muscle rigidity is diagnosed. Patients experience increased heart rate and cardiac arrhythmia. With pathology, convulsions may appear. It is manifested by hyperthermia and epileptic conditions.
There are many symptoms of the disease. If one or more symptoms occur, a person should seek the help of a doctor to diagnose and prescribe an effective treatment regimen.
Diagnostic measures
If vascular blockage is suspected, assessing the history and symptoms is not enough. Therefore, it is recommended to use instrumental methods:
- . This is an x-ray examination that examines the structural elements of the brain. The method detects the location and size of the pathology.
- Angiography. This is an x-ray examination that provides the ability to assess the quality of blood filling of blood vessels. The method determines the time and sequence of filling the vascular system with blood, places where the blood flow is changed due to narrowing or blockage of the lumen channel.

- . It is a full-scale analysis of the structure of brain tissue and blood vessels. The research method determines deviations from the norm that cause abnormal changes.
- . Patients are recommended to undergo duplex scanning of the cervical and intracerebral canals. To study the movement of blood in large canals, Doppler sonography is recommended.
Using echotomography, deep internal tissues are examined. Transcranial Dopplerography allows you to examine the blood flow in the intracranial vessels.
- Neurosonography. Using this method, the state of the brain and its structure in young children is assessed before the fontanel on the head closes. Through it, the vascular network is examined using an ultrasound machine.

- Rheoencephalography. Makes it possible to analyze the state of the vascular network. The level of elasticity, fullness and patency of blood vessels is assessed.
- Electroencephalography. Makes it possible to check the functional side of the circulatory system in the brain structures.
Diagnosis of the disease must be comprehensive, which will have a positive effect on the effectiveness of treatment.
Features of treatment
Only the doctor can decide what to do in case of pathology. It determines methods of treating the disease. At the initial stages of treatment of pathology, the use of drug therapy is recommended. Patients are recommended to take:
- Statinov. Treatment of the disease is carried out with Mevakos, Mefacor.
- Vasodilators. For pathology, the use of Cavinton and Actovegin is recommended.
- Simvastatinov. Treatment of the disease is carried out using Actalipid, Zocor, Levomir, Vasilil.
- Fibratov. In case of blockage of blood vessels, it is recommended to take Clofibrate, Atromid, Atromidine.

- Small. With the help of drugs, anion exchange is ensured. For therapy, the use of Cerebrolysin and levocitin is recommended.
- Tranquilizers. Patients are prescribed medications for anxiety. Its relief is carried out with Diazepam and Phenozepam.
- Antidepressants. If the patient has encephalopathy or chronic cerebral ischemia, this requires taking Amitriptyline.

To improve the patient's condition, it is recommended to take antioxidants - vitamins A, C, E, selenium, microelements, multivitamin complexes. If a person’s disease is caused by diabetes or hypertension, then he needs to use drugs to treat them.
If drug therapy is ineffective in advanced cases, the use of surgical techniques is recommended.
Carotid endarterectomy is highly effective. During the operation, the pathologically altered vessel is dissected and the cholesterol plaque is removed.

In order to restore the vascular wall, sutures are applied. The surgical intervention is performed by a surgeon using local anesthesia. One day after removal of the plaque, the patient is discharged. To treat the disease, a modern method is used - angioplasty.
. This surgical intervention involves inserting a special tube into the vessel, which helps to expand the blocked area. If a patient is diagnosed with vascular blockage, then stenting is performed.
Treatment of the pathological condition requires the use of diet therapy. Patients are strictly prohibited from consuming pickled and smoked foods. Sweets, cocoa and chocolate should also be avoided. Salt intake should be carried out in minimum quantities. It is recommended to use vegetable oil for cooking.

The human diet should be developed on the basis of grapefruits and seaweed. Eggplants that are steamed will be useful. Before eating vegetables, it is recommended to remove the skin from them. The consumption of apples, feijoyas, and gooseberries is recommended.
Proper nutrition will lead to lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels in the blood. To cleanse the blood vessels, it is recommended to drink one glass of hot water in the morning after waking up.
Blockage of blood vessels in the brain is a serious pathology that leads to undesirable consequences. When symptoms of the disease appear, the patient is prescribed treatment using diet therapy, medication and surgical methods. The choice of a specific treatment method depends on the severity of the pathology.
Diseases of the cardiovascular system still occupy one of the leading places among ailments leading to death or disability. A decrease in the patency of blood vessels negatively affects the quality of work not only of individual organs, but also of the entire body. One of the most dangerous manifestations that can occur in the cardiovascular system is blockage of blood vessels in the brain, lower limbs and hearts.
What it is?
Blockage(or occlusion) is a sudden occurrence of vascular obstruction, which is a consequence of pathological processes occurring in the tissues. As a rule, the reasons for the onset of the development of the disease are the appearance of a blood clot or traumatic exposure. At critical moments, when the patient requires urgent surgical intervention, it is the cause of the disease that will be the main criterion in determining the strategy of action of health workers. Weakening or cessation of blood circulation in any part of the circulatory system leads to ischemia (oxygen starvation) of organ tissues and the onset of necrotic processes (we are talking about cell death and tissue necrosis). Therefore, in the event of a complete blockage of a vein or artery, emergency medical care is an absolute necessity.
Symptoms of vascular blockage
If the vessel is passed less than halfway, the person begins to feel obvious discomfort. The symptoms of the disease will depend on where in the circulatory system the clogged fragment is located.
- Blockage of heart vessels. In case of damage to the coronary vessels of the heart, the development of coronary artery disease (CHD) begins. At the initial stage, it is indicated by angina attacks, the duration of which does not exceed 10 minutes.
- Blockage of blood vessels in the legs. If there are such deviations, the patient feels pain and discomfort in the legs. In addition, patients often complain of constant coldness of the legs and pallor or cyanosis of the tissue.
- Blockage of cerebral vessels. In this case, the intensity of the attack will depend on how much the internal cavity is dug. The patient may experience periodic or constant headaches, accompanied by increased blood pressure. Dizziness, vomiting, nausea, or confusion may also occur.
Get a free consultation
Consultation on the service does not oblige you to anything.
Consequences of the disease
A decrease in patency can have the most unpleasant consequences for the patient. The consequences of a developing disease can be very diverse and, again, will depend on the location of the damaged vessel.
So, at the initial stage * blockage of blood vessels in the extremities * is fraught only with the appearance of pain and pulling sensations in the legs. Prolonged obstruction entails the formation of trophic ulcers and complete tissue necrosis. With such a diagnosis, the patient is indicated for limb amputation. Otherwise, he may develop gangrene.
Prolonged ischemia of the heart vessels often causes the development of myocardial infarction. The extent of tissue damage in this case will depend on the volume of the area affected by the obstruction.
Long-term blockage of blood vessels in the brain is no less dangerous. Increased blood pressure and headaches caused by ischemia of brain tissue often indicate the onset of an ischemic attack, the final stage of which may be a stroke.
Diagnostics
 A patient whose complaints indicate the presumed presence of poor patency will have to undergo a series of general and specific examinations to confirm or refute the diagnosis. Along with laboratory research blood and other standard manipulations, the patient may also be prescribed an MRI of the heart and blood vessels related to the area affected by the disease. The resulting three-dimensional image will allow you to determine the degree of vascular patency and identify the presence of plaques or traumatic injuries to veins and arteries.
A patient whose complaints indicate the presumed presence of poor patency will have to undergo a series of general and specific examinations to confirm or refute the diagnosis. Along with laboratory research blood and other standard manipulations, the patient may also be prescribed an MRI of the heart and blood vessels related to the area affected by the disease. The resulting three-dimensional image will allow you to determine the degree of vascular patency and identify the presence of plaques or traumatic injuries to veins and arteries.
MRI of the brain vessels will allow the doctor to get a complete picture of the state of the brain tissue and take timely measures to exclude death or permanent disability.
Treatment of vascular blockages
In the presence of blockage, early detection of the disease is of enormous importance. If there are only primary symptoms, it is possible to eliminate the disease with the help of medications. The intensity and duration of the course will be determined by the doctor, guided by the patient’s condition, age, and the speed of development of the disease.
In the later stages, drug therapy has virtually no results and can only be used to relieve symptoms. In most cases, in later stages, the patient requires surgery. The patient undergoes cleaning of the internal cavities of blood vessels or removal of affected areas of the circulatory system. In particularly advanced cases, specialists may resort to amputation of limbs.
In order not to push your body to the extreme, it is recommended to prevent the disease throughout your life: eat right, give up overeating and bad habits, subject your body to regular physical activity and try to avoid unnecessary stress.
Make an appointment
Make an appointment and get a quality examination in our center
The performance, intellectual potential and mental abilities of a person largely depend on the saturation of the brain vessels with useful nutrients and oxygen, which the human brain receives through the blood vessels. Healthy vessels have elasticity and good blood flow to areas of the brain.
Clinical picture of cerebrovascular disease
When blockage of blood vessels occurs, caused by unfavorable factors, a pathology occurs in which the capacity of the blood vessels decreases, thereby reducing the supply of nutrients necessary for normal brain function.
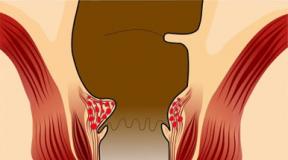
In humans, blood vessels consist of three layers, each of which performs specific functions.
The inner layer consists of epithelial cells that ensure the free passage of blood inside the vessel. The middle layer consists of elastic cells and muscle fibers that prevent blood from spreading outside the vessel. The third layer, the outer layer, is responsible for separating the vessels from the surrounding tissues.
Blockage of blood vessels in the brain occurs due to accumulation in the inner layer plaque cholesterol, gradually their number increases and begins to interfere with the free passage of blood flow, blood circulation decreases, and the vessel loses its elastic mobility due to a decrease in the elasticity of the inner layer, which contributes to the destruction of the integrity of the blood vessel and the formation of blood clots.
Long-term blockage of blood vessels in the brain can cause the development, or lead to insufficient blood supply, which can lead to a stroke.
There are more and more people diagnosed with blockage of blood vessels in the brain every year; the reasons for the manifestation of this disease are the consumption of fatty foods, alcohol abuse, nicotine and poor diet. The accumulation of cholesterol plaques or Atherosclerosis affects the largest vessels responsible for the blood supply to the brain.
Chronic inflammation also leads to deformation and blockage of blood vessels in the brain. In many cases, these are two main factors in the narrowing of blood vessels in the brain.
Symptoms of blockage of blood vessels in the brain
The disease occurs in two scenarios, acute, which includes the occurrence of a stroke, which, without providing timely assistance, leads to the death of the patient, and according to the scenario chronic course a disease that lasts for several years. A person can get used to the symptoms of the chronic form and eventually stop noticing them.
The chronic course of the disease of blockage of blood vessels in the brain has three stages:
- With the first, the elasticity of the walls of blood vessels begins to decrease, which causes headaches, irritability appears, concentration decreases and fatigue increases.
- At the second stage, the symptoms of the disease intensify, often accompanied by tinnitus and sleep disturbances or insomnia. All together, this leads to memory impairment, fainting, disruption of the musculoskeletal system, and possible false urge to urinate. Sometimes a patient with blockage of cerebral vessels experiences visual impairment and sensitivity in the extremities.
- The third stage is the most distinct in terms of symptoms; as it develops, it becomes difficult for the patient to move, coordination of movements is lost, and mental ability is inhibited. Due to disturbances in brain activity, a person may experience uncontrolled urination and defecation.
In the third stage, the patient needs constant assistance, as he almost completely loses his ability to work and cannot control his actions. Failure to provide assistance at this stage of the disease often leads to immobility of the patient.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of the disease must be done in several directions. A neurologist examines neurological symptoms, assessing the degree of mental activity of the patient and reflexes. To assess the severity of the disease and the accuracy of the diagnosis, the doctor needs the help of relatives who observe the patient’s behavior at home.
ECG and computed tomography of the brain, along with Doppler sonography and computed tomography, are among the most important tools in identifying the disease. They allow you to find out the speed of blood flow, the presence of blood clots, aneurysms and atherosclerotic plaques in the vessels.
Treatment methods for blockage of blood vessels in the brain
 When treating blockage of cerebral vessels, one must proceed from the clinical picture (stage of the disease). The acute form of the disease requires immediate intervention by specialists and the prescription of medications that reduce or eliminate the symptoms of the disease. With this form it is possible rapid blockage of blood vessels, which will lead to irreversible consequences in the human brain.
When treating blockage of cerebral vessels, one must proceed from the clinical picture (stage of the disease). The acute form of the disease requires immediate intervention by specialists and the prescription of medications that reduce or eliminate the symptoms of the disease. With this form it is possible rapid blockage of blood vessels, which will lead to irreversible consequences in the human brain.
Detection of the disease in the chronic stage requires the appointment of therapy and complex treatment from cardiologists, therapists, angioneurologists. At this stage, the patient’s cure depends on the patient’s compliance with all procedures and on correctly selected drug therapy. In particularly difficult cases drug treatment can last a lifetime.
If there is no positive effect after taking medications, it is necessary surgical intervention. The purpose of the surgical intervention is to restore healthy blood flow into the vessel; for this, bypass surgery or endarterectomy is performed.
During bypass surgery, a special stent is inserted into the patient’s vessel, which opens the normal flow of blood into the vessels of the brain. And with endarterectomy, atherosclerotic plaques are removed.
Disease Prevention
To prevent blockage of blood vessels in the brain, it is recommended healthy eating, you should exclude foods high in fat and salt from your daily diet. Eat vegetables and fruits more often, because the acids they contain contribute to the breakdown of fats. Provide your body with constant physical activity, stop smoking, and reduce the consumption of strong alcohol. And also avoid stress or reduce its impact on your nervous system.