Ostomy surgery. Features of the operation to close a colostomy and possible complications. Encyclopedia Ileostomy Types of ileostomy and their features
With a number of intestinal diseases, the passage of stool and its release through natural means is impossible. Then doctors resort to colostomy.
Colostomy - what is it and how to live with it?
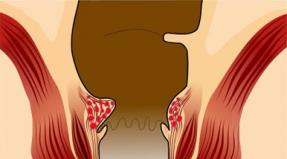
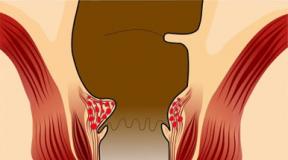
A colostomy is a kind of artificial anus that doctors make in the abdominal wall. A hole is made in the peritoneum, and the end of the intestine (usually the colon) is sewn into it. Feces, passing through the intestines, reach the opening and fall into the bag attached to it.
Typically, such an operation is performed when there is a need to bypass the rectal part in the postoperative period, in case of traumatic injuries or tumors, inflammation, etc.
Photo of rectal colostomy
If the lower intestinal tract cannot be restored, a permanent colostomy is performed. Healthy people can easily control bowel movements. This is ensured by the uninterrupted activity of the sphincters.
In patients with colostomy, feces exit through the artificially formed anus in the form of semi-formed or formed masses, without disturbing intestinal activity.
Indications for colostomy
A colostomy can be temporary or permanent. Children most often undergo a temporary stoma.
In general, the indications for colostomy are as follows:
- Anorectal incontinence;
- Blockage of the intestinal lumen;
- colonic walls such as gunshot or mechanical wounds;
- Severe cases of colonic pathologies such as ischemic colitis, cancer or peritonitis, and nonspecific ulcerative colitis, abscesses of the intestinal walls with perforation, etc.;
- Recurrent cases of cancer processes in and, or;
- The presence of severe forms of post-radiation proctitis, this is especially common after cervical canal cancer;
- If there are internal to the vagina or bladder;
- As a preoperative preparation for the prevention of suture dehiscence and suppuration;
- For congenital anomalies such as Hirschsprung's pathology, meconium ileus in newborns or atresia of the anal canal, etc. (if radical intervention is not possible);
- With rectosigmoid resection, if after the operation the sutures are ineffective.
Types of stoma
Depending on the location, colostomies are classified into several types: transverse, ascending and descending.
- Transverse colostomy.
 A transversostomy is formed in the upper abdomen, in the transverse colon.
A transversostomy is formed in the upper abdomen, in the transverse colon.
To avoid nerve damage, the transverse stoma is placed closer to the left splenic flexure.
A transverse colostomy is indicated for intestinal blockage or oncopathologies, traumatic injuries and diverticulitis, and congenital colon anomalies.
Typically, such colostomies are installed temporarily for the duration of treatment. On a permanent basis, transverse stomas are necessary when removing an underlying section of intestine.
Transverse stomas are divided into two types: single-barrel and double-barrel.
- Single-barrel or the end stoma is a longitudinal incision of the large intestine, so only one opening is brought to the surface. This technique is usually permanent and is used in radical ectomy of the descending colon.
- Double-barreled A colostomy involves removing a loop of intestine and making a transverse incision on it in such a way that 2 intestinal openings are exposed to the peritoneum. Through one passage feces are excreted, and through the other they are usually injected. medications.
The lower intestine may continue to produce mucus, which will be released through the hole created by the cut or the anus, which is normal. Such transversostomies are usually made for a certain period of time.
- Ascending colostomy or ascendostomy.
A similar stoma is located on the ascending colon, so it is localized on the right side of the peritoneum. This area is located in the early intestinal part, therefore the excreted contents will be alkaline, liquid and rich in residual digestive enzymes.
Therefore, the colostomy bag needs to be cleaned as often as possible, and the patient is advised to drink more to avoid dehydration, since an ascendostomy is characterized by thirst. An ascending colostomy is usually a temporary therapeutic measure.
- Descending and sigmoid colostomy method (descendostomy and sigmostoma).
These types of colostomies are installed on the left side of the peritoneum in its lower part, actually at the end of the colon. Therefore, it produces masses with physical and chemical properties similar to ordinary feces.
A distinctive feature of such colostomies is the patient’s ability to regulate bowel movements. This is explained by the fact that in these parts of the intestine there are nerve endings that allow you to control the process of stool release. Such localization of colostomies allows them to be installed for a long time and even permanently.
Advantages and disadvantages
 The procedure is often vital in nature, providing the patient with a normal life after radical surgical intervention for cancer of the sigmoid or rectum.
The procedure is often vital in nature, providing the patient with a normal life after radical surgical intervention for cancer of the sigmoid or rectum.
This fact is the main indisputable advantage of the artificially created anus.
In addition, modern bandages, colostomy bags and other devices allow you to live comfortably even with a permanent colostomy.
The method certainly has its drawbacks. Perhaps the main one is the psychological factor, which is often the cause of deep depression in the patient. But doctors have learned to deal with this too - they carry out explanatory work with patients, talk about proper stoma care, clarify important nuances, talk about sensations, etc.
For many, smell may seem like another drawback. But the problem is completely solvable, because modern colostomy bags are equipped with magnetic covers, anti-odor filters, and there are also specialized deodorants on sale. Therefore, today such accessories allow us to solve the problem of skin irritation and frequent replacement of the colostomy bag.
Types of colostomy bags
Colostomy bags come in one- and two-component types. Two-component ones are equipped with ostomy bags and a self-adhesive plate, connected by a special flange. But such colostomy bags are inconvenient because they can cause skin irritation. Therefore, when using them, it is allowed to replace the plate once every 2-4 days, and the bag - daily.
If there is a feeling of itching and discomfort, it is recommended to immediately peel off the plate. An undoubted advantage is that the colostomy bag is equipped with a special filter that eliminates gases and odors.
Unlike a two-component one, a one-component colostomy bag must be changed every 7-8 hours. Two-component ones involve replacing only the bag, and the plate is changed only once every 3-4 days.
The drainage bag must be emptied when it is 1/3 full; to do this, bend over the toilet a little and open the drainage hole, after which the feces bag must be washed and dried. Before reusing the bag, check the drainage hole to ensure it is closed.
How to care for your stoma at home?
A colostomy requires very careful care, which begins from the first day after surgery. First, the patient is taught by a nurse who changes colostomy bags and irrigates the stoma. In the future, the patient independently changes fecal bags and treats the stoma opening.
The whole process takes place in several algorithms:
- First, the feces are removed;
- Then the outlet hole is washed with boiled warm water, the skin around it is thoroughly washed, and then dried with gauze napkins;
- Treat the skin surface with Lassara paste or Stomagesiv ointment, after which gauze soaked in Vaseline is applied around the stoma and covered with a sterile bandage and cotton wool. Cover the treatment area with a gauze bandage, which is changed every 4 hours.
- When the stoma heals and is completely formed, you can use colostomy bags. The final formation and healing is indicated by the mouth not protruding above the skin and the absence of inflammatory infiltrate. Only with such a clinical picture is the use of a colostomy bag allowed.
- It is recommended to change fecal bags in the evenings or in the morning. First, carefully remove the used feces receptacle, then remove any remaining feces and wash the stoma. Then the mouth and the skin around it are treated with ointment or paste, and then the colostomy bag is fixed again.
Typically, Coloplast paste containing a small amount of alcohol is used to glue the receiver. The product does not cause irritation even to skin damaged by trauma and inflammation, and also improves the fixation of the device.
Some patients, before gluing the colostomy bag, treat the skin with a special protective film, which protects the skin from inflammation and irritation.
Nutrition
 There is no special specialized diet for colostomy patients, so after surgery, significant changes in the patient’s diet are not expected.
There is no special specialized diet for colostomy patients, so after surgery, significant changes in the patient’s diet are not expected.
With a colostomy, the only thing that needs to be taken into account is the effect of each product on the digestive processes.
- It is recommended to limit foods that promote gas formation, which include eggs and beer, carbonated drinks and cabbage, mushrooms and legumes, onions and chocolate, for obvious reasons.
- Foods such as garlic and eggs, spices and fish, onions and cheese noticeably enhance the smell of intestinal gases.
- Lettuce and yogurt, lingonberries and spinach, parsley, etc. have the opposite effect.
With the right combination of products, many unpleasant situations can be avoided. In addition, it is recommended to chew food with special care, eat more often and little by little.
To prevent unwanted gas escape, you can lightly press on the stoma. Colostomy patients should also monitor the consumption of laxatives and constipation foods to avoid problems such as diarrhea or constipation.
Types of operations
The location of the colostomy is determined by the doctor, taking into account the specific clinical picture every patient.
The presence of hems or scars can significantly complicate the installation of a stoma on the intestine, since it is necessary to take into account the condition of the fatty tissue and muscle layer, which, when folds form, can displace the colostomy over time.
Patients may require surgery to create or close a colostomy, as well as surgical intervention for reconstructive purposes. Each intervention has its own individual characteristics, requiring a different approach to the patient.
Overlay
The colostomy procedure is performed under general anesthesia in a sterile operating room.
- First, the surgeon cuts off a rounded area of subcutaneous tissue and skin at the site of the intended location of the stoma.
- In the second stage of the operation, the muscles are separated in the direction of the fibers. To avoid compression on the intestine, the hole is made large enough. In addition, the likelihood that the patient will gain excess weight is taken into account in advance if the stoma is applied for a long time.
- Then the intestine is brought out through a loop and the necessary incision is made on it.
- The intestine is sutured to the muscle tissue of the peritoneum, and its edges are attached to the skin.
Unfortunately, it has not yet been possible to invent drainage means into the stomal mouth, since the immune system includes protective functions and actively resists foreign materials, provoking degeneration and inflammation of tissues.
Only surgical suturing of the intestinal edge to the skin heals favorably, although it would be much easier to use special tubes coming from the intestinal lumen and brought out.
Closing
 Surgery to close a stoma in the intestine is called a colostomy.
Surgery to close a stoma in the intestine is called a colostomy.
A temporary colostomy is usually closed 2-6 months after placement. This operation is the elimination of an artificially created anus.
A prerequisite for closing the operation is the absence of obstructions in the lower parts of the intestine to the anus.
About a centimeter from the edge of the stoma, the surgeon makes a tissue dissection, slowly separating the elements. Then the intestine is brought out and the edge with the hole is excised. Then both ends of the intestine are sutured and returned to the peritoneum. Then, using contrast, the seam is checked for leaks, after which the wound is sutured layer-by-layer.
Reconstructive surgery
Typically, such interventions are prescribed to patients with temporary colostomies imposed while the underlying sections of the intestine are being treated. Many patients believe that after stomal closure, intestinal functions are completely restored, which is not entirely true.
Even if the restorative surgical intervention is completely successful, the absence of a certain area in the intestine cannot but affect its further functionality.
The most optimal period for stromal closure is the first 3-12 months after surgery. This is the only way to count on successful healing of intestinal tissues without consequences for the body. In fact, reconstructive surgery is the closure of a stoma or colostomy, the description of which is presented above.
Diet after surgery
After reconstructive surgery or closure of the stoma, you must follow a strict diet so that the digestive processes quickly recover.
The diet comes down to excluding foods like:
- Hot seasonings or spices like curry, chili pepper, etc.;
- Excessive amounts of soda, kvass or beer;
- Gas-forming products such as beans, garlic or cabbage, etc.;
- Fatty foods;
- Foods that cause irritation of intestinal tissues, such as currants or raspberries, grapes or citrus fruits.
If necessary, the doctor prescribes individual restrictive dietary instructions for the patient.
Complications
Colostomy is a serious surgical procedure that can cause many complications.
- Specific secretions. This mucus is produced by intestinal tissues as a lubricant to facilitate the passage of stool. Normally, the consistency of the discharge may be sticky or similar to egg white. If there are purulent or bloody impurities in the mucus, this may indicate the development of an infectious process or damage to the intestinal tissue.
- Blocking the stoma orifice. Typically, this phenomenon is the result of the adhesion of food particles and is accompanied by watery stools, swelling of the stoma, flatulence or nausea and vomiting symptoms. If you suspect the development of such a complication, it is recommended to exclude solid foods, periodically massage the abdominal area near the mouth of the stoma, increase the volume of fluid consumed, and take hot baths more often, which helps to relax the abdominal muscles.
- Paracolostomy hernia. Such a complication involves protrusion of the intestine through the muscles of the peritoneum, and a clear subcutaneous bulge is observed near the mouth of the stoma. Special support bandages, weight control and avoidance of lifting and dragging heavy objects will help you avoid this. Usually hernias are eliminated using conservative methods, but sometimes it cannot be done without. Unfortunately, there is always a possibility of re-formation of the hernia process.
Also, with a colostomy, other complications may develop, such as fistulas, prolapse or retraction of the stoma, stenosis or ischemia of the colostomy, leakage of digestive waste into the abdominal cavity or onto the skin surface, stricture or evagination, and necrosis, purulent processes, etc.
You can avoid such troubles, the main thing is to strictly follow medical recommendations, especially the diet and hygienic requirements for caring for a colostomy.
Videos about how to care for a colostomy:
A colostomy can be temporary or permanent. Children most often undergo a temporary stoma.
In general, the indications for colostomy are as follows:
- Anorectal incontinence;
- Blockage of the intestinal lumen tumor formation;
- Traumatic injuries colonic walls such as gunshot or mechanical wounds;
- Severe cases of colonic pathologies such as diverticulitis or ischemic colitis, cancer or peritonitis, polyposis and ulcerative colitis, abscesses of the intestinal walls with perforation, etc.;
- Recurrent cases of cancer processes in bladder tissues and the uterus, cervical canal or rectum;
- The presence of severe forms of post-radiation proctitis, this is especially common after radiation therapy for cervical cancer;
- If there are internal fistula from the rectum to the vagina or bladder;
- As a preoperative preparation for the prevention of suture dehiscence and suppuration;
- For congenital anomalies such as Hirschsprung's pathology, meconium ileus in newborns or atresia of the anal canal, etc. (if radical intervention is not possible);
- With rectosigmoid resection, if after the operation the sutures are ineffective.
It is quite obvious that creating a fistula of the colon for the unnatural discharge of feces is a very extreme measure, and it is carried out for health reasons. A colostomy may be temporary or permanent (permanent stoma).
After 2-3 months, in the absence of complications, the operated patient can return to his usual work activity, unless it is associated with heavy physical labor.
The main point in rehabilitation is the right psychological attitude and support from loved ones.
Patients with ostomies lead full lives, attend concerts, theaters, have sex, get married and have children.
In large cities there are societies for ostomy patients, where they provide all kinds of help and support to such people. The Internet provides great assistance in finding information; reviews from patients living with a colostomy are very important.
A tracheostomy is an artificially created hole in the neck with a tube removed, which is installed with the aim of recreating damaged human respiratory functions. If there are disturbances in the functioning of the respiratory system and the impossibility of performing an independent act of inhalation and exhalation, the patient often undergoes an emergency tracheal ostomy.
Epicystoma is removed from Bladder onto the surface of the abdominal wall using a special catheter. The indications for such manipulation are the patient’s inability to urinate naturally for various reasons. There are temporary and permanent epicystostomies.
Surgeries on the rectum are extremely traumatic.
New techniques are being introduced into modern oncological practice to help preserve the act of natural bowel movement and prevent typical postoperative complications.
size and localization of malignant neoplasm; features of the cellular structure of tumor structures; classification of cancer according to the international TNM system.
Resection and its types
Anorectal incontinence; Blockage of the intestinal lumen by tumor formation; Traumatic damage to the colonic walls such as gunshot or mechanical wounds; Severe cases of colonic pathologies such as diverticulitis or ischemic colitis, cancer or peritonitis, polyposis and ulcerative colitis, abscesses of the intestinal walls with perforation, etc.
(if it is not possible to carry out radical intervention); With rectosigmoid resection, if after the operation the sutures are ineffective.
Since surgery for malignant tumors is a life-saving operation, the only contraindication to it is the very serious condition of the patient. Quite often, such patients actually arrive at the hospital in serious condition (cancer cachexia, anemia), but preoperative preparation for some time makes it possible to prepare such patients.
Despite the fact that it is difficult to predict how the body will behave after the removal of an organ, much depends on the patient himself and his care. Quitting smoking and alcohol is necessary.
For several days after surgery, they are fed intravenously. They are allowed to drink only a little water on their own; after 3 days, tea with a small cracker made from wheat flour is introduced into the diet; when the body adapts, the diet is expanded with puree soup and omelet; then porridge, grated vegetables, fish soufflé are introduced; on the tenth day, new products are introduced, observing the body's reaction; you will have to forget about fried, fatty and smoked foods forever.
Before you enter New Product, you should consult your doctor. Limits flour, starches, spices, whole milk, sweets.
It is important that the diet contains proteins, fats, carbohydrates and sugars are minimized. Food is taken in small portions every 2 hours; you need to drink at least a liter of water per day.
Food intake at night is limited - only a glass of low-fat kefir is allowed. Vitamin and mineral complexes are often prescribed additionally.
twisted boiled lean fish and meat; low-fat dairy products are acceptable, except whole milk; crackers, vegetarian soups, unsweetened fruits and steamed dishes are allowed.
Removing the pancreas is a difficult decision, the goal of which is to save a life.
Even if the prognosis is favorable, further life will require medical supervision and medication for the rest of your life. But this operation gave many people the opportunity to live.
Preparing for surgery
Registration: 05/18/2015 Messages: 6
Hello! Please tell me how to quickly restore the functioning of the rectum and its sensitivity after an operation to remove a stoma? Uncontrolled and liquid evacuation occurs from the anus. How long will uncontrolled emptying last? What exercises should you do, what diet?
Registration: 10/16/2003 Messages: 4,520
How long has the rectum been “unemployed”?
As I understand it, you did not perform any training on the rectal stump before the reconstructive surgery?
And immediately before the operation (when they began to plan it) - too?
And why is the stool loose? Did fluid also flow through the stoma before the operation?
Perhaps there is dysbiosis, then means that improve the microflora. Adsorbents.
Thank you very much for the answer.
Kishka was unemployed for six months.
The patient is placed in a comfortable position lying on his back. In addition to the usual skin preparation, the skin around the artificial anus is carefully shaved, and a sterile gauze pad is inserted into the colostomy opening.
Progress of the operation
Holding a piece of gauze in the intestinal lumen, an oval incision is made through the skin and subcutaneous tissue around the colostomy. The surgeon inserts his or her index finger into the stoma as a guide to prevent cutting through the bowel wall or peritoneal opening while the skin and subcutaneous tissue are separated using blunt and sharp techniques.
In cases where the stoma has already been in effect for some time, before proceeding with closure, the ring of scar tissue at the junction of the mucous membrane and the skin should be excised. Continuing to hold the index finger in the lumen of the intestine, the surgeon makes an incision with scissors around the edge of the mucous fold.
This incision is made through the seromuscular layer down into the submucosa, taking care to create separate layers for closure. By pulling the edge of the mucous membrane with tweezers, it is closed in the transverse direction to the longitudinal axis of the intestine.
Use a continuous Connell-type suture made of thin catgut or interrupted sutures made of thin 0000 silk on a French needle. After closing the mucous membrane, the previously created serous-muscular layer, freed from fat, is brought together with interrupted Halstead sutures made of thin silk.
After the stoma is removed, the wound is washed several times, and clean towels are placed around the wound. All instruments and materials are removed, gloves are changed, and the wound is closed only with clean instruments.
The closed part of the intestine is held on one side, while separating the adjacent fascia with curved scissors. The separation of the fascia from the intestine is facilitated by exposure of the silk sutures previously placed to secure the intestine during the colostomy.
With this method of closure, the peritoneal cavity is not opened. The surgeon checks the patency of the intestine with his thumb and forefinger.
If a small hole was accidentally made in the peritoneum, it is carefully closed with interrupted sutures made of thin silk. The wound is washed repeatedly with warm saline solution.
The suture line is pressed with forceps while the edges of the overlying fascia are approximated with interrupted 00 silk sutures. A rubber drain can be removed at the lower corner of the wound.
The subcutaneous tissue and skin are closed in layers as usual. Some people choose not to have the skin covered because of the possibility of infection.
After radical surgery, many patients eat approximately the same foods as before surgery. However, some foods can cause discomfort and therefore should be included in the daily diet only 2-3 months after surgery.
Depending on the stage of the process, the location of the tumor and other characteristics, one of the types of surgical intervention is prescribed: resection (cutting off), extirpation (removal), amputation. Resection is the removal of a segment of the rectum. For malignant tumors in the rectum, anterior, abdominal-anal resection and Hartmann resection are performed.
Anterior resection is indicated when the malignant neoplasm is located in the upper ampullary or rectosigmoid portions of the rectum. As a rule, it is performed for a tumor detected at an early stage.
Surgical intervention consists of mobilizing and cutting off part of the rectum and sigmoid colon with their subsequent connection. The anastomosis is created manually using interrupted sutures in two rows or using a special device.
As a result of such surgical intervention, the functions of the anal sphincter are preserved, that is, the creation of a colostomy - an artificial anus - is not required. Abdominal-anal resection is performed for cancer of the upper and middle ampullary sections of the rectum.
Tests: general blood tests, urine tests, biochemical analysis blood, coagulogram, determination of blood group and Rh factor. Study of markers of infectious diseases - viral hepatitis, syphilis, HIV.
Electrocardiogram. X-ray of the chest organs.
Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs. Examination by a therapist.
For women - examination by a gynecologist. To more accurately determine the extent of the tumor, an MRI of the pelvic organs may be prescribed.
A biopsy of the tumor is required to determine the extent of tissue removal (for less differentiated types of tumors, the boundaries of the tissue removed should be expanded).
oncology; necrosis (death) of tissue; rectal prolapse or prolapse of the intestine without the ability to set the organ back and with the ineffectiveness of conservative treatment methods.
spleen, gall bladder, upper stomach.
The operation to remove the pancreas is as follows. The doctor opens the abdominal cavity in the area of the pancreas. Depending on the severity of the disease, part of the pancreas or the entire organ is removed, as well as other organs damaged by the disease. Next, the incision is sutured and secured with special staples.
To avoid complications after surgery, the patient is prescribed a strict diet. In the first days after surgery, the patient must fast. He is allowed to drink about 1.5 liters of pure, non-carbonated water per day. The daily intake of water should be divided into several servings and drunk in small sips.
After a few days, unsweetened tea and steamed egg white omelet are allowed into the patient’s diet. You can eat buckwheat or rice porridge cooked in water or low-fat milk.
After a week, you can add a small amount of bread, low-fat cottage cheese and butter to your diet. Vegetable soups, especially those made from cabbage, will be beneficial. Before using, all the ingredients of the soup must be thoroughly ground.
The main principle of the diet after removal of the pancreas is the maximum content of proteins in dishes and the almost complete absence of fats and carbohydrates. You should reduce your salt intake to no more than 10 grams per day and completely stop eating sugar. In any case, the patient should know exactly what can be eaten with pancreatitis of the pancreas.
The entire daily diet should be divided into 5-6 meals. Portions should be small. They should be consumed slowly, chewing thoroughly. Food should contain a large amount of vitamins. Additionally, it is recommended to take vitamins and minerals in tablets. Particular attention to the water regime of the body. The daily water intake after surgery should be 1.5-2 liters.
After removal of the pancreas, you should completely stop smoking and drinking alcohol. Also limit the consumption of potatoes, sweets, flour, carbonated drinks and strong coffee. Eating fatty, fried and smoked foods is strictly not recommended.
In addition to proper nutrition and following a strict diet, you should avoid any stress, since the removal of an organ is already a great stress for the body.
Besides, important role food plays. You can live a long time without pancreas if you follow a strict diet.
The first days after the operation the patient is forced to fast. Doctors only allow drinking non-carbonated mineral water.
You need to drink a liter of liquid per day, but not all at once, but in small portions. After a few days, they are allowed to drink a little tea, unsalted soup and an omelet made from only proteins, steamed.
You can eat buckwheat or rice porridge, but they must be cooked in water or milk. After a week, you can add some bread, butter and cottage cheese to your diet.
Vegetable soups without cabbage are also allowed. They must be thoroughly ground before use.
Types of stoma
The ileostomy operation, as you remember, is performed for various indications (cancer, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, abdominal trauma, diverticula, bleeding, intestinal obstruction, etc.), so here we will consider general recommendations on nutrition, and the subtleties regarding your disease, you need to check with your doctor.
In all cases, unless specifically instructed, you should avoid eating certain foods for the first 4-6 weeks after your ostomy.
Foods that should be excluded from the diet of a patient with an ileostomy
- The diet should not contain meat or poultry with skin (hot dogs, hot dogs, sausage), meat with spices, shellfish, peanut butter, nuts, fresh fruits (except bananas), juices with pulp, dried fruits (raisins, prunes, etc.) .d.), canned fruits, canned pineapples, frozen or fresh berries, coconut flakes;
- The diet prohibits “heavy eating”: raw vegetables, boiled or raw corn, mushrooms, tomatoes, including stewed ones, popcorn, jacket potatoes, fried vegetables, sauerkraut, beans, legumes and peas;
- Avoid dairy mixed with fresh fruits (except bananas), berries, seeds, and nuts. Nut rolls, poppy seeds, bran, sesame seeds, dried fruits or berries, whole grain cereals, spice grains, berries, herbs such as peppers, cloves, whole anise seeds, celery seeds, rosemary, cumin seeds, and herbs ;
- The diet should not contain jams, jellies with seeds, or carbonated drinks
With a colostomy, there are no digestive problems like with an ileostomy. In general, there should be a “regular, normal balanced diet, with a fluid volume of about 1.5 liters.”
With a colostomy, the stool is thicker and, as a rule, does not require a special diet or medical manipulation. Diet involves the patient's active participation in determining what is right for him and what is not.

The patient himself understands which foods cause him discomfort, abdominal pain and gas formation, and avoids them. The issue of fiber in the diet of patients with colostomy is decided individually; in some patients, fiber improves the function of the stoma, while in others, on the contrary, it causes abdominal pain and gas.
Constipation with a colostomy is not uncommon. Sometimes the cause of constipation during a colostomy is narcotic analgesics or other medications.
Also, constipation during a colostomy can be caused by a lack of fluid. For constipation during a colostomy, they first resort to diet correction; adding fruits and vegetables to food usually helps to cope with stool retention and does not require supplementing therapy with laxatives.
Sometimes you have to give an enema for a colostomy. This is described in the article about colostomy care.
Depending on the location, colostomies are classified into several types: transverse, ascending and descending.

A transversostomy is formed in the upper abdomen, in the transverse colon.
To avoid nerve damage, the transverse stoma is placed closer to the left splenic flexure.
A transverse colostomy is indicated for intestinal blockage or oncopathologies, traumatic injuries and diverticulitis, and congenital colon anomalies.
Progress of the operation
temporary double-barreled colostomy
It is most convenient to form a colostomy from the transverse or sigmoid colon, which have a long mesentery; they are quite easy to remove into the wound.
The incision for colostomy is made separately from the main laparotomy incision.
The skin and subcutaneous layer is excised using a circular incision. The aponeurosis is dissected crosswise. The muscles are separated. The parietal peritoneum is incised, its edges are sutured to the aponeurosis. This creates a tunnel for the removal of the intestine.
A hole is made in the mesentery of the mobilized intestine, and a rubber tube is inserted into it. By pulling the ends of the tube, the surgeon removes a loop of intestine into the wound.
A plastic or glass rod is inserted in place of the tube. The ends of the stick are placed on the edges of the wound, the loop of intestine seems to hang on it. The intestinal loop is sutured to the parietal peritoneum.
After 2-3 days, when the parietal and visceral peritoneum have fused, an incision is made into the withdrawn loop (pierced, then incised with an electric knife). The length of the incision is usually 5 cm. The posterior uncut wall of the intestine forms the so-called “spur” - a septum separating the proximal and distal knee of the stoma.
With a correctly formed double-barreled colostomy, all fecal matter is removed through the adductor end to the outside. Mucus may be released through the distal (outflow) end of the intestine, and medications can be administered through it.
The loop of intestine is sharply separated from the skin and other layers of the abdominal wall. The edges of the bowel defect are refreshed and the defect is sutured.
A loop of intestine is immersed into the abdominal cavity. The peritoneum and abdominal wall are sutured in layers.
The ostomized portion of the intestine is separated from the skin. Intestinal clamps are applied to both ends of the loop.
A section of intestine with an exposed loop is resected and an end-to-end or end-to-side anastomosis is performed.
The most common reason for a permanent colostomy is cancer of the lower and middle ampullary rectum. With such a localization of the tumor, it is almost impossible to perform surgery while preserving the anal sphincter.
In this case, treatment according to oncological criteria is considered radical: the tumor itself and regional lymph nodes are removed as widely as possible. If there are no distant metastases, the patient is considered cured, but...he will have to live without a rectum.
Therefore, the quality of the patient’s life directly depends on the quality of the formed colostomy.
After the stoma is placed, it takes some time for the intestine to heal. Therefore, the patient receives only parenteral nutrition for several days. You are allowed to drink liquid every other day.
On the 3rd day after surgery, you are allowed to take liquid and semi-liquid foods.
Adapting to a stoma will take some time (from several months to a year).
The intestinal wall exposed to the skin will be swollen for some time after the operation. It will gradually decrease in size (stabilize in a few weeks). The mucous membrane of the excreted intestine is red.
Touching the stoma during care does not cause pain or discomfort, since the mucous membrane has almost no sensitive innervation.
The first time after surgery, feces will be released continuously. Gradually, you can achieve their release several times a day.
There is no special diet for ostomy patients. Food should be varied and rich in vitamins.
It is advisable to eat at strictly defined times 3 times a day. The bulk of food should be consumed in the morning, followed by a less dense lunch and a lighter dinner. Drink enough liquid (at least 2 liters). Food must be chewed thoroughly.
After a few months of adaptation, the patient himself will learn to determine his diet and select those products that will not cause discomfort. At first, it is advisable to eat foods that do not contain toxins (boiled meat, fish, semolina and rice porridge, mashed potatoes, pasta).
People with ostomies, like everyone else, can experience constipation or diarrhea. Usually, sweet, salty, fiber-containing foods (vegetables, fruits), brown bread, fats, cold foods and drinks enhance peristalsis. Mucous soups, rice, white crackers, cottage cheese, pureed cereals, black tea reduce peristalsis and retain stool.
You should avoid foods that cause increased gas formation: legumes, vegetables and fruits with peels, cabbage, carbonated drinks, baked goods, whole milk. Some foods produce an unpleasant odor when digested, which is very important in case of possible involuntary release of gases from the stoma. These are eggs, onions, asparagus, radishes, peas, some types of cheese, beer.
Transverse colostomy.
gastrostomy; intestinal: ileostomy, colostomy; tracheostomy; epicystostomy.
The shape is convex and retracted. There are single-barreled and double-barreled. Depending on the duration of use: temporary and permanent.
Every few hours, the outer tube should be washed with sodium bicarbonate solution (4%) to remove any remaining mucus from the cavity. To prevent the formation of skin inflammation and diseases, it is necessary to treat the area around the tracheosome.
To do this, moisten cotton balls in a bowl with a solution of furatsilin. Then, using tweezers, they blot the area of skin around the tracheostomy.
After which zinc ointment or Lassara paste is applied. The treatment is completed by applying sterile wipes.
Secure the bandage with adhesive tape. It is periodically recommended to suction out the contents of the trachea, since often patients with a tracheostomy cannot fully cough, which leads to stagnation of mucus and, as a result, difficulty breathing.
To carry out this manipulation, you need to sit the patient on the bed and perform a manual chest massage. Pour 1 ml of sodium bicarbonate (2%) into the trachea through the tube to thin the mucus.
Then you need to insert a tracheobronchial catheter into the tube. By attaching a special suction, remove the mucus from the trachea.
Proper care of the stoma is extremely important, since disruption of its functions can lead to respiratory arrest.
A gastrostomy is removed from the abdominal area to provide a person with nutrition in cases where the patient is unable to eat on his own. Thus, liquid or semi-liquid nutrition is introduced directly into the stomach.
Most often, this condition is temporary, for example, with serious injuries and in the postoperative period. Therefore, gastrostomy in rare cases is permanent.
When the function of independent food intake is restored, the gastrostomy tube is closed surgically.
Gastric stoma - what is it, in what cases is it established? When a gastrostomy is applied, a rubber tube is brought out, intended directly for transporting food into the stomach. During feeding, insert a funnel for convenience, and in between meals, clamp the tube with a thread or clothespin.
With a gastrostomy, the main goal of care is to treat the skin around the hole in order to prevent skin inflammation, diaper rash, and rash. The area of skin around the stoma is treated first with furatsilin solution using cotton balls and tweezers, and then with alcohol. After which it is lubricated with aseptic ointment. The procedure is completed by applying a bandage.
Treatment of cancer after surgery for a diagnosis of rectal cancer (or repeated malignant lesions of the rectum) is reduced to alleviating symptoms and prolonging the patient’s life.
Surgical method.
In the intensive care unit, a person returns from anesthesia to a normal state. After the operation, the patient is prescribed analgesics to relieve discomfort and pain in the abdominal cavity.
The doctor may prescribe injection anesthesia (epidural or spinal). To do this, drugs that relieve pain are introduced into their body using droppers.
A special drainage is placed in the area of the surgical wound, which is needed to drain the accumulated excess fluid, and after a couple of days it is removed.
Depending on what type of colon surgery is performed, the patient will have a different recovery period, treatment and rehabilitation plan after the operation. To avoid complications and dangerous consequences, patients are advised to undergo preparation and cleansing procedures, which are agreed upon with the doctor, and if the patient experiences discomfort, it is necessary to immediately report it.
Breathing exercises
Rehabilitation includes performing breathing exercises. The patient performs inhalations and exhalations under the supervision of a doctor, because they affect well-being, and incorrect execution will lead to worsening of the condition, nausea, and vomiting.
Breathing exercises are important in cases where the patient has had a major operation and needs a long recovery period. Proper breathing will prevent the development of pneumonia and respiratory problems.
After colon surgery, the doctor prescribes medications that help get rid of pain and inflammation. These are analgesic drugs that are classified by type, depending on the intensity of the effect.
Physiotherapy
Physical activity will help restore organ function, improve digestion, regulate weight and improve condition during the rehabilitation process. The sooner the patient begins to move, the easier it is to start the body.
But you need to remember that not everyone is recommended to do the exercises right away. If the patient's condition is severe or moderate, the doctor will first recommend doing light warm-up exercises, but they are performed lying down, without exerting effort.
When the patient’s health improves, the nausea subsides, the temperature drops, the doctor will select another set of physical activity. You need to force yourself to warm up regularly, then recovery will be faster.
In approximately every third patient, which is 25% of the total number, distant metastases are detected when cancer is detected. In 19% of patients, cancer is detected at stages 1-2. And only 1.5 patients learn about the diagnosis during preventive examinations. A large number of neoplasms occur at stage 3. Approximately 40-50% of patients are carriers of tumors with distant metastases.
The survival prognosis for rectal cancer is 5 years. This includes about 60% of cancer patients.
Residents of the USA, Canada and Japan are most affected by the disease. IN Lately Rectal cancer has become a widespread cancer in the Russian Federation.
So, according to statistics, out of every 100 thousand population, 16 thousand suffer from rectal cancer. Moscow and St. Petersburg became the hotbed cities for morbidity.
There is no clear answer to the question “How many people live with a disease such as colorectal cancer”. Patients live only as long as the tumor approaches the boundaries of the mucous layer.
If it does not cross the border, then 88% of patients will be able to live more than 5 years. However, we should not forget that the only prognostic factor is the presence/absence of regional metastases.
Thus, the likelihood of regional metastases in young people is much higher than in other patients with this tumor.
medical examination; endoscopic examination of the rectum - rectoscopy; rectal digital examination of the anus.
Once every six months, it is recommended to undergo the following diagnostic measures: ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs and fluorographic examination of the lungs. If there are suspicious symptoms of resumption of the disease, it is important, without waiting for exacerbations, to undergo a full diagnosis using computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.
Rectal cancer
Colorectal cancer is one of the most common cancers of the gastrointestinal tract. This pathology ranks 4th in the domestic structure of the incidence of malignant tumors in men (5.7%) and 2nd place in women (7.2%).
The patient's recovery rate after surgery depends on the type of surgery and the volume of intestine removed.
Breathing exercises
All surgical patients are always prescribed breathing exercises: forced inhalations, exhalations, or inflating a balloon. Such exercises help adequately ventilate the lungs and prevent the development of complications (bronchitis, pneumonia). Breathing exercises should be done as often as possible, especially if the period of bed rest is prolonged.
Anesthesia
The duration of taking analgesics and their type depends on the severity of the pain syndrome, which is often determined by the type of operation (laparotomy or laparoscopic). After open interventions, patients usually receive intramuscular narcotic analgesics (for example, droperidol) for the first 1-2 days, then are transferred to non-narcotic drugs (ketorolac).
After laparoscopic operations, recovery is faster, and while still in the hospital, many patients are transferred to tablet forms of drugs (ketanov, diclofenac).
Postoperative sutures are inspected and processed every day, and the bandage is also changed frequently. The patient should monitor the scars and try not to scratch or get them wet. If the stitches begin to come apart, become red and swollen, bleeding develops, or the pain is too severe, you should immediately inform the medical staff.
Physiotherapy
The approach to each patient is strictly individual. Of course, both the patient and the doctor are interested in early verticalization (the ability to stand up) and independent walking. However, the patient receives permission to even sit up in bed only when his condition really allows it.
At first, a set of tasks is assigned to perform while lying in bed (some movements with the arms and legs). Then the training scheme is expanded, exercises are gradually introduced to strengthen the abdominal wall (after the surgeon makes sure that the stitches are intact).
When the patient begins to walk independently, the set of exercises includes walking around the ward and corridor for a total duration of up to 2 hours.
Physiotherapy
It is extremely rare to do without surgery
Immediately after the operation, the patient is placed in the intensive care unit, where the functions of the heart, breathing, and gastrointestinal tract will be carefully monitored for 1-2 days.
A tube is inserted into the rectum, through which the intestinal lumen is washed with antiseptics several times a day.
Within 2-3 days the patient receives parenteral nutrition, after a few days it is possible to take liquid food with a gradual transition to solid food over two weeks.
To prevent thrombophlebitis, special elastic stockings are put on the legs or elastic bandages are used.
Painkillers and antibiotics are prescribed.
Main complications after rectal surgery
Bleeding. Damage to neighboring organs. Inflammatory suppurative complications. Urinary retention. Dehiscence of anastomotic sutures. Postoperative hernias. Thromboembolic complications.
If a complete extirpation of the rectum with the formation of a permanent colostomy (unnatural anus) is to be performed, the patient should be warned about this in advance. This fact usually shocks the patient, sometimes to the point of categorically refusing the operation.
For the first 4-6 weeks after rectal surgery, the consumption of coarse fiber is limited. At the same time, the problem of preventing constipation becomes urgent.
It is allowed to eat boiled meat and fish, steamed cutlets, stale wheat bread, soups with weak broth, porridges, vegetable purees, stewed vegetables, casseroles, dairy products, taking into account milk tolerance, pasta dishes, eggs, fruit purees, jelly.
Drinks - tea, herbal infusions, non-carbonated mineral water.
The volume of liquid is at least 1500 ml per day.
Gradually, the diet can be expanded.
The problem of preventing constipation is urgent, so you can eat wholemeal bread, fresh vegetables and fruits, rich meat broths, dried fruits, and sweets in small quantities.
Patients with a colostomy usually experience discomfort with excessive gas, so they should be aware of foods that can cause increased gas: milk, brown bread, beans, peas, nuts, carbonated drinks, beer, baked goods, fresh cucumbers, radishes, cabbage, onions and some other products.
Even in the absence of complications, the rehabilitation process after removal of the pancreas takes a long period of time, but the prognosis is favorable. After the operation, a strict diet, large amounts of medication and insulin injections are prescribed.
It will take a lot of time for the body to recover. The patient will be tormented by painful sensations for a long time. However, they can be minimized by taking painkillers. The moral support of family and friends may be much more important for the patient.
Acute pancreatic necrosis. A state of almost instantaneous death of the organ parenchyma due to the release of proteolytic enzymes.
The iron actually “melts” under the influence of its own juice. If the patient does not undergo immediate surgery, he will die from septic shock.
Malignant neoplasm. The most common cancer is the head of the pancreas.
In the early stages of the disease, you can limit yourself to resection of the affected part of the organ, but with rapid progression of the disease, it is necessary to remove it entirely. Alcohol abuse.
It is very rare to find such pronounced damage to the gland by derivatives of the standard. In most cases, patients suffer from problems with the liver and esophageal varices.
However, there are situations when alcoholism leads to necrosis of the parenchyma. Blockage of the excretory ducts with stones.
Calculous pancreatitis rarely causes complete removal of an organ, but can significantly aggravate the patient’s condition. It is necessary to carry out stone elimination and symptomatic treatment.
It is important to understand that pancreatectomy is an extremely radical step. It is impossible to accurately predict its consequences. That is why it is possible to decide on it only in a critical situation when it comes to a person’s life. If there is the slightest chance to save an organ, you should try to do so.
Strict adherence to the diet. Without careful monitoring of your diet, it will be impossible to achieve any satisfactory results.
It is prohibited to eat any fatty, fried or smoked food. Basically, you can only eat dietary foods that are easily digestible.
Since the main digestive organ has been removed and they need to eat, patients are required to artificially replace proteolytic substances with tablets. Formation of type 1 diabetes mellitus.
This consequence of the elimination of the gland develops in 100% of patients. It requires treatment with insulin injections and a strict diet.
Psychological disorders. One of the most important points to work on.
Often people who have undergone surgery do not want to exist like this. They withdraw and isolate themselves from others and feel inferior.
At this stage, it is necessary to help such patients, to make them understand that many people in the world live well with the same problem.
Related Posts
Removing the pancreas is a radical solution. Under what conditions is surgery to remove the gland justified?
Can a person live without a pancreas? How will the surgery affect your quality of life? What to do after removal? The answers to these and other questions are presented in the article.
There are partial and complete removal of the organ. In case of significant damage to an organ or a large tumor, when partial removal does not help, the entire gland is removed.
There are two types of removal operations. If the tumor is localized in the head of the gland, then the head with a fragment of the small intestine is removed.
Often it is necessary to remove part of the stomach with the gallbladder and lymph nodes. If the formation is in the tail, then the tail, the body of the gland, and the spleen with vessels are removed.
It is difficult to predict in advance how the operation will go.
bleeding; infection; pancreatitis.
Even if there are no complications, long-term rehabilitation is necessary. For the body to recover, it takes time and strict adherence to the doctor’s instructions. After organ removal, insufficient production of hormones is often observed.
In addition to physical condition, the psychological attitude is important. It is difficult to overestimate the need for moral support, because surgery is stressful for the body.
Removal of the pancreas leads to diabetes mellitus, metabolic disorders. The modern level of medicine allows a person to live even without such an important organ.
In this case, it is necessary to adhere to a strict diet, monitor health status, frequent tests, lifelong hormone replacement therapy (enzyme preparations - insulin or glucagon), and adherence to bed rest.
If the pancreas was only partially removed, the remaining part of the organ compensates for the lost function.
Perhaps insulin and hormones will not be needed, and you can limit yourself to diet, a healthy lifestyle, and blood sugar control.
3 Risk of complications
Despite following all medical instructions, complications may develop in the postoperative period. Most often, skin irritation (or periostomal dermatitis) appears.
A rash may appear near the excretory tube, accompanied by itching or burning. As a rule, such complications are observed in patients who did not immediately learn how to correctly cope with the task at hand - processing an artificial hole.
An allergic reaction to the drugs used during treatment should not be ruled out.
Advantages and disadvantages
The procedure is often vital in nature, providing the patient with a normal life after radical surgical intervention for cancer of the sigmoid or rectum.
This fact is the main indisputable advantage of the artificially created anus.
Nutrition
In order for macro and microelements to be better absorbed, you need to chew your food thoroughly, this will not only improve digestion, but also reduce the likelihood of blockage of the gastrointestinal tract. Eat small meals 5-6 times a day. The diet should include fats, vitamins, proteins, carbohydrates and minerals.
There is no special specialized diet for colostomy patients, so after surgery, significant changes in the patient’s diet are not expected.
With a colostomy, the only thing that needs to be taken into account is the effect of each product on the digestive processes.
The patient's diet must be complete, containing a certain amount of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Foods included in the diet should be rich in vitamins and minerals, which is why fruits and vegetables are so necessary.
Spicy, sour and fatty foods are completely excluded from the patient's diet, and meat dishes are limited. The role of a full breakfast and thorough chewing of each piece is great.
Meals should include at least five meals, and the portion size should be controlled: they should be small.
Any patient perceives the closure of a colostomy with joy, because he has a chance, although not immediately, to send his needs through the anus, located at the end of the rectum, and not on the stomach, and to do this at his own request. However, to achieve the long-awaited normalization of stool, you need to go a long way to restore the functioning of the large intestine. How is the operation to close a colostomy performed and when will the period of life associated with many inconveniences, called life after a colostomy, end?
A colostomy has some advantages over an ileostomy:Unlike an ileostomy, a colostomy is an opening for removing feces from the large intestine.
- Although uncontrollable, the urge to defecate is an opportunity to mentally prepare in a few minutes.
- The feces are practically formed - the skin around the stoma is subject to less irritation.
- The course of the operation to apply a colostomy, just like the course of the operation to close it, consists of fewer stages.
- The diet is not so strict.
- The recovery period takes 2-3 times less time than if a stoma for the small intestine is closed.
 The course of the operation to close a colostomy consists of the following stages:
The course of the operation to close a colostomy consists of the following stages:
- With a double-barreled stoma, an incision is made between two holes, and with a single-barrel stoma, the length of the incision depends on the length of the longitudinal incision of the colon, which was made before the colostomy.
- The section of intestine where the ostomy was performed is removed.
- With double-barrel, the holes are sutured, and with single-barrel, the functioning ends of the intestine are connected. As a rule, the closure of an end stoma (single-barrel type) is carried out with the removal of a section of the intestine that was cut longitudinally, plus 10-15% beyond this length, and this is already a resection of the intestine, that is, the intestine will not function as before the ostomy. The consequences are expressed in rapid bowel movements from 15 minutes to 2 hours after eating. Accordingly, to increase digestibility useful substances, you need to either eat several times more, or switch to high-calorie and frequent meals 5 times a day or more. Therefore, the procedure for closing a double stoma is easier for the surgeon and the patient than for closing a single stoma.
- The muscle tissue is carefully sewn together and the top suture is applied. Sutures are applied with self-absorbing threads such as catgut.
- The degree of tightness of the intestinal section is checked.
The operation may include additional steps, such as transplanting a section of the rectum or another section of the large intestine if a suitable donor is available.
The operation to remove a colostomy lasts on average 100-120 minutes, and in some cases up to 3 hours. Despite the fact that reconstructive surgery is entrusted only to professionals, due to the physiological characteristics of the body of some patients, for example, heart problems, colostomy and stoma elimination, it can be carried out in 2 stages with a break of several days. If the patient cannot withstand the action general anesthesia, then the colostomy is not closed until the heart can cope with the required load.
It is possible to completely restore the former functionality of the intestines in 40% of cases. Often, after closing a colostomy, complications may arise both in the area of the stoma where the surgical actions were performed, and in the functioning of the intestine after a long period. The main complications arise when removing a single-barrel (end colostomy, since this type is not temporary.)
 When removing both single-barrel and double-barrel stoma, the following complications may occur:
When removing both single-barrel and double-barrel stoma, the following complications may occur:
- Perforation or rupture of the intestine in the stoma area.
- Rectal prolapse.
- Suppuration or inflammation in the area of the former stoma.
- The occurrence of obstruction in the ostomy area due to the accumulation of feces in the area of the sutures.
- if the sphincter muscles have atrophied or been damaged;
- after a long course of chemotherapy;
- if the villous epithelium is atrophied or damaged by more than 50%, fecal stasis with subsequent sepsis is possible;
- if during the stoma more than 30% of the intestinal tract was removed, except for the output from the rectum.
Recovery
As a rule, the complications described above arise when restorative procedures are not properly performed in the postoperative period, which can last from several weeks to several months.
The end date of the postoperative rehabilitation complex can only be announced by the attending physician after diagnosing the intestinal condition.
Postoperative rehabilitation includes an appropriate diet and a strict daily routine.
The diet looks like this:- the first 3-5 days after surgery - droppers with the necessary substances;
- 5-12 days – liquid porridge with sugar;
- 12-21 days – foods, except raw vegetables and fruits, are gradually introduced into the diet;
- raw cabbage, apple peels, fried and spicy foods, as well as legumes and corn should not be consumed for 90 days or longer after surgery.
If some diseases are left untreated, the patient may develop complications that can only be eliminated through surgery.
In such cases, experts resort to a method called.
What it is?
A colostomy is usually understood as an artificial anus. During surgery, doctors connect it to the abdominal wall and bring it out through the peritoneum.
The resulting feces move along the intestinal tract, reach the designated passage and fall into a specialized pouch.
Often, such surgical intervention is performed at the moment when there is a need to bypass the rectal area at the postoperative stage, in case of injury, tumor formation and the development of inflammatory processes.
If it is not possible to completely normalize the lower intestine, then the colostomy becomes permanent.
A healthy person can easily control the processes of emptying the digestive canal. The sphincter is responsible for this.
The operation to close a colostomy can be short-term or continuous. In childhood, a short-term colostomy is often installed.
Indications for use include:
- clogging of the intestinal passage with tumors;
- injuries to the intestinal walls as a result of gunshot or mechanical damage;
- the presence of serious pathologies in the form of diverticulitis, cancerous tumors, ischemic colitis, polyposis, ulcerative colitis, abscesses of the intestinal walls, perforation;
- recurrence of cancer in the urinary and uterine tissue structures, cervical canal or rectum;
- the presence of complicated proctitis after radiation treatment for cervical canal cancer;
- formation of internal to the vagina or bladder;
- preoperative preparations for suture dehiscence and suppuration;
- development of congenital anomalies in the form of Hirschsprung's disease, meconium obstruction in newborns, underdevelopment of the anus;
- performing rectosigmoid resection when the sutures are unstable.
Intestinal operations can be performed urgently when the patient's condition is complicated by adverse consequences.

Types of surgery
The location of the colostomy is determined only by the doctor based on symptoms and test results. The presence of scars can complicate the placement of an ostomy. It is also worth considering the condition of the fat layer and muscle structures.
Patients may undergo a colostomy or closure. Intervention is also carried out using a reconstructive method. Each form of manipulation has its own specifics and requires a specific approach.
Overlay
This type of manipulation is performed under general anesthesia.
- The operation scheme is as follows:
- The doctor makes a small incision that touches not only the skin, but also the subcutaneous tissue.
- The second stage is based on the separation of muscle structures according to the direction of the fibers. To avoid squeezing the digestive canal, the hole is made large. In addition to all this, the weight of the patient and the duration of the stoma are taken into account.
- The intestine is brought out with loops and a small incision is made on them.
- After this, the intestine is sutured to the muscle fiber of the peritoneum, and the edges are fixed to the skin.
The immune system resists for a long time, as it perceives all manipulations as foreign bodies. This can lead to tissue depletion and inflammation, so regular treatment is required.

Closing
Operations to close a stoma are commonly called colostomies. A short-term colostomy is closed only two to six months after the application. This type of surgery involves the elimination of an artificially created anorectal meatus.
The main condition is the absence of barriers to the lower areas of the intestinal tract to the anus.
The operation scheme is based on the following:
- Approximately one centimeter from the edge of the stroma, tissue structures are dissected and adhesive elements are separated. All movements must be slow and careful.
- Then the intestine is taken out and the edge is cut off together with the hole.
- After this, both ends of the intestine are sutured and returned back to the abdominal area.
- Using contrast, the seam is checked for tightness. If everything is normal, then the wound is sutured.
Reconstructive and restorative manipulations
This type of surgical intervention is prescribed for patients with a temporary colostomy, which is applied to the lower parts of the intestine. Many patients think that after the stoma is closed, digestive functionality returns completely to normal. But it is not so.
Even if everything went well, it may happen that some area has lost its ability to work.
The most optimal period for closing a colostomy is considered to be the first three to twelve months after the procedure.

Only in such cases can one hope for successful tightening of intestinal tissues without complications.
Following a diet after the procedure
Life after a colostomy involves following a strict diet to restore bowel function.
- Proper nutrition excludes from the diet:
- hot seasonings and spices;
- excessive consumption of carbonated drinks, kvass and beer;
- gas-forming products in the form of beans, garlic and cabbage;
- fatty and fried foods;
food that provokes irritation of intestinal tissue structures. These include currants, raspberries, grapes, and citrus fruits.
To make rehabilitation go faster, food intake is completely excluded in the first two days. You can only wet your lips with warm water.

If the patient’s condition is normal, then water and liquefied foods should be introduced into the diet. It is better to eat little by little, but often. Food must be boiled or steamed. At the same time, dishes should contain a minimum of salt.
Adverse consequences
Secretion of a specific nature
Intestinal tissue structures produce mucus, which acts as a lubricant to facilitate the movement of bowel movements. When a section of the anus is removed and a colostomy is performed, sticky mucus is released, which is similar to egg white.
But after the liquidation of the organ, complications may arise in the form of the appearance of purulent or bloody streaks. This process indicates infection or damage to intestinal tissue.
Blocking the stoma orifices
Adverse consequences may include blocking the stoma orifice. This phenomenon occurs as a result of the adhesion of food particles. Then the patient will complain of loose stools, swelling of the stoma, flatulence, nausea and vomiting.
If the patient suspects the development of complications, it is advised to completely exclude solid foods from the diet, and also massage the abdominal area near the mouth of the stoma. Restorative measures include consuming large amounts of fluid and taking hot baths. These processes will help relax the abdominal muscle structures.

Paracolostomy hernia
This type of complication involves protrusion of the intestinal canal through the muscular peritoneal tissue. In this case, lumps form under the skin near the mouth of the stoma.
Special bandages that support the abdominal muscles will help to avoid the development of adverse consequences. You should also carefully monitor your weight and avoid lifting heavy objects.
Often, hernias are removed using conservative methods. But in some situations, urgent surgical intervention is required.
The postoperative period may result in other unpleasant complications in the form of fistulas, prolapse or anomaly of the colostomy, narrowing of the intestine, ischemia, leakage of waste into the abdominal area, obstruction of the digestive tract, tissue necrosis and purulent processes.
It is possible to restore the functioning of the organ and avoid the development of serious complications, but only in that situation if you follow all the doctor’s recommendations. Medical recommendations include mandatory hygienic measures in the area of colostomy and adherence to a strict diet.